데이터 열기¶
오픈소스 소프트웨어 생태계의 일원으로서, QGIS는 서로 다른 라이브러리들을 기반으로 빌드되어, 자체 제공자와 결합해 다음과 같은 여러 포맷들을 읽고, 많은 경우 작성할 수도 있는 능력을 갖추고 있습니다:
Vector data formats include ESRI formats (Shapefile, Geodatabase…), MapInfo and MicroStation file formats, AutoCAD DWG/DXF, GeoPackage, GeoJSON, GRASS, GPX, KML, Comma Separated Values, and many more… Read the complete list of OGR vector supported formats.
Raster data formats include ArcInfo Binary Grid, ArcInfo ASCII Grid, JPEG, GeoTIFF, ERDAS IMAGINE, MBTiles, R or Idrisi rasters, ASCII Gridded XYZ, GDAL Virtual, SRTM, Sentinel Data, and many more… Read the complete list of raster supported formats.
Database formats include PostgreSQL/PostGIS, SQLite/SpatiaLite, Oracle, DB2 or MSSQL Spatial, MySQL…
Support of web data services (WM(T)S, WFS, WCS, CSW, ArcGIS Servers…) is also handled by QGIS providers (see OGC 데이터 클라이언트로서의 QGIS).
보존된(archived) 폴더에서 지원하는 파일을 읽어올 수 있고, 가상(virtual) 및 메모리 레이어 같은 QGIS 자체 포맷도 사용할 수 있습니다.
As of the date of this document, more than 80 vector and 140 raster formats are supported by the GDAL/OGR and QGIS native providers.
참고
Not all of the listed formats may work in QGIS for various reasons. For
example, some require external proprietary libraries, or the GDAL/OGR
installation of your OS may not have been built to support the format you
want to use. To see the list of available formats, run the command line
ogrinfo --formats (for vector) and gdalinfo --formats (for raster),
or check menu (for raster)
in QGIS.
In QGIS, depending on the data format, there are different tools to open it,
mainly available in the menu
or from the Manage Layers toolbar (enabled through menu).
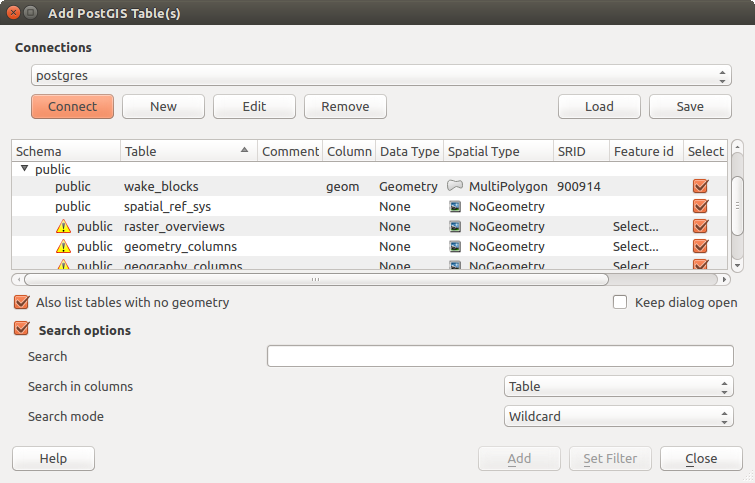
However, all these tools point to a unique dialog, the Data Source
Manager dialog that you can directly open with the  Open Data Source Manager button available on the Data Source
Manager Toolbar or by pressing Ctrl+L. Indeed, the Data Source
Manager dialog offers a unified interface to open vector or raster file-based
data as well as databases or web services supported by QGIS. It can be set
modal or not with the
Open Data Source Manager button available on the Data Source
Manager Toolbar or by pressing Ctrl+L. Indeed, the Data Source
Manager dialog offers a unified interface to open vector or raster file-based
data as well as databases or web services supported by QGIS. It can be set
modal or not with the  Modeless data source manager dialog
in menu.
Modeless data source manager dialog
in menu.
QGIS Data Source Manager dialog¶
Beside this main entry point, you also have the  DB Manager
plugin that offers advanced capabilities to analyze and manipulate connected
databases. More information on DB Manager capabilities are exposed in DB Manager Plugin.
DB Manager
plugin that offers advanced capabilities to analyze and manipulate connected
databases. More information on DB Manager capabilities are exposed in DB Manager Plugin.
There are also many other tools, native or third-party plugins, that help you open dedicated data formats.
This chapter will describe only the tools provided by default in QGIS to load data. It will mainly focus on the Data Source Manager dialog but more than describing each tab, it will also explore the tools based on the data provider or format specificities.
탐색기 패널¶
The Browser is one of the main ways to quickly and easily add your data to projects. It’s available as:
a Data Source Manager tab, enabled pressing the
 Open Data Source Manager button (Ctrl+L);
Open Data Source Manager button (Ctrl+L);as a QGIS panel you can open from the menu (or
 ) or by pressing Ctrl+2.
) or by pressing Ctrl+2.
In both cases, the Browser helps you navigate in your file system and manage geodata, regardless the type of layer (raster, vector, table), or the datasource format (plain or compressed files, database, web services).
The context menu for an element in the Browser panel is opened by right-clicking on it.
For file system directory entries, the context menu offers the following:
Add as a Favorite
Properties…
Hide from Browser
Fast Scan this Directory
New Directory…
Open Directory
Favourites, can also be removed and renamed:
Rename favourite…
Remove favourite
For leaf entries that can act as layers in the project, the context menu will have a selection of entries. For example, for non-database, non-service-based vector, raster and mesh data sources:
Add Selected Layer(s) to Canvas
Properties…
Delete File 《<name of file>》…
In the Layer properties entry, you will find (similar to what you will find in the vector and raster layer properties once the layers have been added to the project):
Metadata for the layer. Metadata groups: Information from provider (if possible, Path will be a hyperlink to the source), Identification, Extent, Access, Fields (for vector layers), Bands (for raster layers), Contacts, Links (for vector layers), References (for raster layers), History.
A Preview panel
The attribute table for vector sources (in the Attributes panel).
To add a layer to the project using the Browser:
Enable the Browser as described above. A browser tree with your file system, databases and web services is displayed. You may need to connect databases and web services before they appear (see dedicated sections).
Find the layer in the list.
Use the context menu, double-click its name, or drag-and-drop it into the map canvas. Your layer is now added to the Layers panel and can be viewed on the map canvas.
팁
Open a QGIS project directly from the browser
You can also open a QGIS project directly from the Browser panel by double-clicking its name or by drag-and-drop into the map canvas.
파일을 불러들이고 나면, 맵 둘러보기 도구를 이용해서 맵을 이동 및 확대/축소할 수 있습니다. 레이어 스타일을 변경하려면, 레이어 명을 더블 클릭해서 Layer Properties 대화창을 열거나 범례에 있는 레이어 명을 오른쪽 클릭한 다음 컨텍스트 메뉴에서 을 선택하십시오. 벡터 레이어의 심볼을 설정하는 작업에 대해 더 자세히 알고 싶다면 Symbology Properties 을 참조하세요.
탐색기 패널 상단에 있는 아이콘의 기능은 다음과 같습니다:
 Add Selected Layers: 레이어의 컨텍스트 메뉴에서 를 선택해도 맵 캔버스에 데이터를 추가할 수 있습니다.
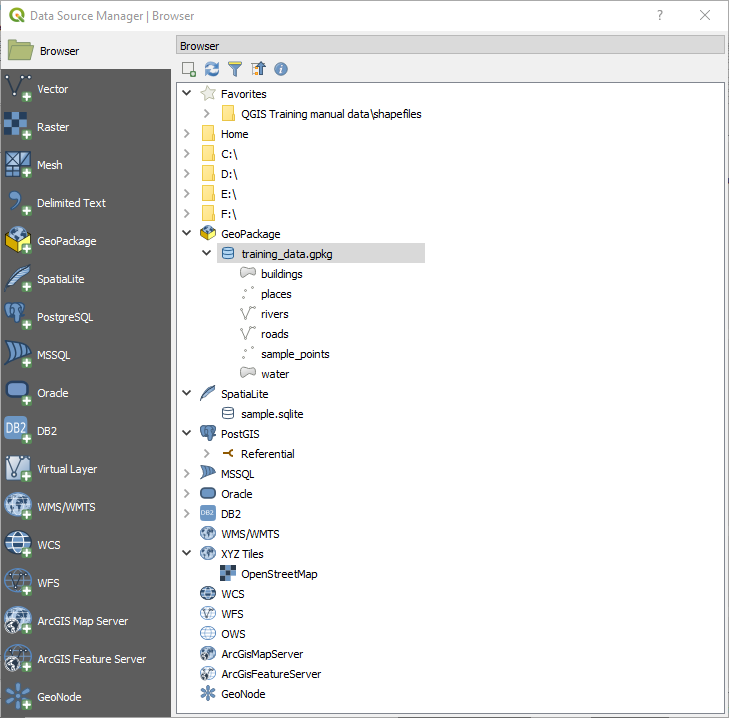
Add Selected Layers: 레이어의 컨텍스트 메뉴에서 를 선택해도 맵 캔버스에 데이터를 추가할 수 있습니다. Filter Browser: 특정 데이터를 검색합니다. 검색어 또는 임의 문자 기호(wildcard)를 입력하면 탐색기가 트리를 필터링해서 입력 문자열과 일치하는 데이터베이스 테이블, 파일명 또는 폴더를 가리키는 경로만 표시합니다. 일치하지 않는 다른 데이터 또는 폴더는 숨깁니다. 나란히 있는 QGIS 탐색기 패널 그림의 Browser Panel(2) 예시를 참조하십시오. 필터링 작업은 대소문자를 구분할 수도 있고 안 할 수도 있습니다. 다음 옵션으로 필터링을 설정할 수도 있습니다:
Filter Browser: 특정 데이터를 검색합니다. 검색어 또는 임의 문자 기호(wildcard)를 입력하면 탐색기가 트리를 필터링해서 입력 문자열과 일치하는 데이터베이스 테이블, 파일명 또는 폴더를 가리키는 경로만 표시합니다. 일치하지 않는 다른 데이터 또는 폴더는 숨깁니다. 나란히 있는 QGIS 탐색기 패널 그림의 Browser Panel(2) 예시를 참조하십시오. 필터링 작업은 대소문자를 구분할 수도 있고 안 할 수도 있습니다. 다음 옵션으로 필터링을 설정할 수도 있습니다:normal: 검색어를 포함하는 모든 항목을 반환합니다.
wildcard(s) 이용: 검색 문자열에서 위치를 지정하는
?그리고/또는*문자를 이용해서 검색을 세밀하게 조정합니다.regular expression 이용
 Enable/disable properties widget: when toggled on,
a new widget is added at the bottom of the panel showing, if applicable,
metadatas of the selected item.
Enable/disable properties widget: when toggled on,
a new widget is added at the bottom of the panel showing, if applicable,
metadatas of the selected item.
탐색 트리에 있는 항목을 오른쪽 클릭하면 다음 작업을 할 수 있습니다:
파일 또는 테이블인 경우, 해당 항목의 메타데이터를 표시하거나 사용자의 프로젝트에 항목을 열 수 있습니다. 테이블의 경우 재명명하거나, 삭제하거나, 추출할 수도 있습니다.
폴더인 경우, 사용자의 즐겨찾기에 북마크해두고 탐색 트리에서 숨길 수 있습니다. 탭에서 이렇게 숨긴 풀더들을 관리할 수 있습니다.
데이터베이스 또는 웹 서버로의 연결을 생성할 수 있습니다.
스키마를 새로고침하거나, 재명명하거나 삭제할 수 있습니다.
단순히 드래그&드롭하는 것만으로 데이터베이스로 파일을 불러들이거나 어떤 스키마/데이터베이스에서 다른 스키마/데이터베이스로 테이블을 복사할 수도 있습니다. 드래그하는 동안 오래 스크롤을 해야 하는 일을 피하기 위해 두 번째 탐색 패널을 사용할 수 있습니다. 그냥 파일을 선택한 다음 한쪽 패널에서 다른 패널로 드래그&드롭하십시오.

나란히 있는 QGIS 탐색기 패널¶
팁
사용자 OS의 파일 탐색기에서 단순히 드래그&드롭하는 것만으로 QGIS에 레이어 추가
사용자의 운영체제 파일 탐색기에서 Layers Panel 또는 맵 캔버스로 파일(들)을 드래그&드롭해서 프로젝트에 추가할 수도 있습니다.
데이터베이스 관리자¶
DB Manager 플러그인은 하나의 사용자 인터페이스에서 QGIS가 지원하는 공간 데이터베이스 유형(PostGIS, SpatiaLite, GeoPackage, Oracle Spatial, MSSQL, DB2, 가상 레이어)을 통합하고 관리하기 위한 자체 도구이자, QGIS의 주 도구 가운데 하나이기도 합니다. 메뉴에서 이 플러그인을 활성화시킬 수 있습니다.
 DB Manager 플러그인은 다음 여러 기능들을 제공합니다:
DB Manager 플러그인은 다음 여러 기능들을 제공합니다:
데이터베이스에 연결해서 그 구조 및 내용을 표시합니다.
데이터베이스의 테이블을 미리보기합니다.
맵 캔버스에 레이어를 더블 클릭 또는 드래그&드롭으로 추가합니다.
QGIS 탐색기 또는 다른 데이터베이스로부터 데이터베이스에 레이어를 추가합니다.
SQL 쿼리의 산출물을 생성하고 맵 캔버스에 추가합니다.
가상 레이어 를 생성합니다.
DB Manager Plugin 에서 데이터베이스 관리자에 관한 더 자세한 정보를 설명하고 있습니다.

데이터베이스 관리자 대화창¶
제공자 기반 불러오기 도구¶
QGIS가 유형에 상관없이 레이어를 추가하기 위해 제공하는 주 도구인 탐색기 패널 및 데이터베이스 관리자 이외에도, 데이터 제공자에 특화된 도구들이 존재합니다.
참고
일부 외부 플러그인 도 QGIS에서 특정 파일 포맷을 열기 위한 도구를 제공합니다.
파일에서 레이어 불러오기¶
파일에서 레이어를 다음과 같이 불러올 수 있습니다:
for vector data (like Shapefile, Mapinfo or dxf layer), click on
 Add Vector Layer toolbar button, select the
Add Vector Layer toolbar button, select the
 Add Vector
Layer menu option or press Ctrl+Shift+V.
This will bring up a new window (see figure_vector_add) from which you can
check
Add Vector
Layer menu option or press Ctrl+Shift+V.
This will bring up a new window (see figure_vector_add) from which you can
check  File and click on Browse. You can
also specify the encoding for the file if desired.
File and click on Browse. You can
also specify the encoding for the file if desired.
벡터 레이어 추가 대화창¶
래스터 레이어의 경우,
 Add Raster Layer 아이콘을 클릭하거나,
Add Raster Layer 아이콘을 클릭하거나,  Add Raster Layer 메뉴 옵션을 선택하거나, Ctrl+Shift+R 조합 키를 누르십시오.
Add Raster Layer 메뉴 옵션을 선택하거나, Ctrl+Shift+R 조합 키를 누르십시오.
표준 파일 열기 대화창(OGR 지원 벡터 레이어 열기 대화창 그림 참조)이 열릴 겁니다. 이 창에서 파일 시스템을 둘러보고 shapefile, GeoTIFF 또는 다른 지원 데이터소스를 불러올 수 있습니다. 선택 상자 Filter  를 통해 몇몇 지원 파일 유형을 사전 선택할 수 있습니다. 잘 검증된 포맷들만 목록에 표시됩니다.
를 통해 몇몇 지원 파일 유형을 사전 선택할 수 있습니다. 잘 검증된 포맷들만 목록에 표시됩니다. All files (*.*) 를 선택하면 다른 검증 안 된 포맷들도 불러올 수 있습니다.

OGR 지원 벡터 레이어 열기 대화창¶
Selecting a file from the list and clicking Open loads it into QGIS.
More than one layer can be loaded at the same time by holding down the
Ctrl or Shift key and clicking on multiple items in the dialog.
Figure_vector_loaded shows QGIS after loading the alaska.shp file.
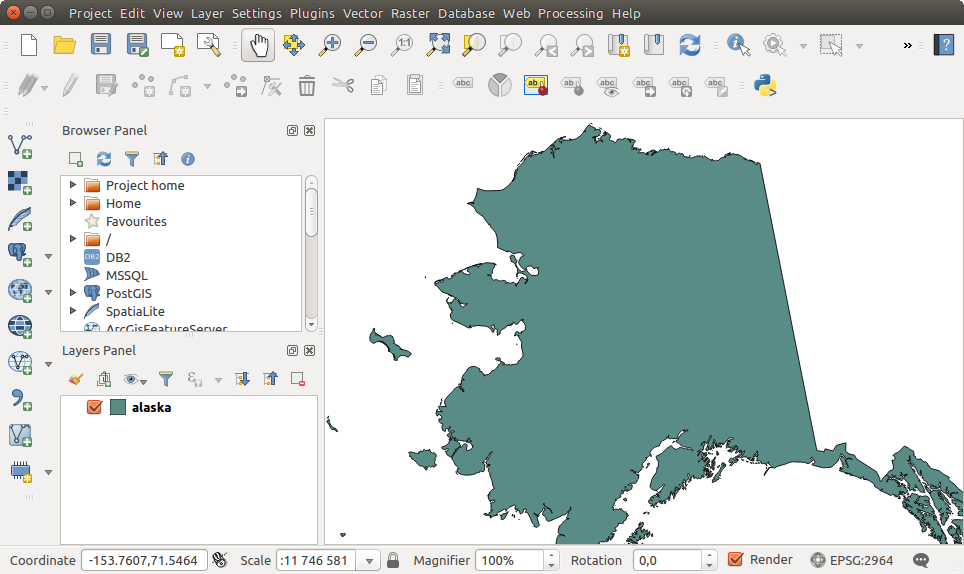
알래스카 shapefile을 불러들인 QGIS¶
참고
MapInfo(예를 들면 .tab) 또는 Autocad(.dxf) 같은 일부 포맷은 파일 하나 안에 서로 다른 도형 유형을 함께 담을 수 있기 때문에 QGIS에 이런 포맷을 불러올 경우, 레이어 하나 당 도형 유형 하나만 보유할 수 있도록, 사용할 도형을 선택할 수 있는 대화창이 열립니다.
Using the  Add Vector Layer tool:
Add Vector Layer tool:
You can also load specific formats like
ArcInfo Binary Coverage,UK. National Transfer Format, as well as the raw TIGER format of theUS Census BureauorOpenfileGDB. To do that, you’d need to select Directory as Source type. In this case
a directory can be selected in the dialog after pressing Browse.
Directory as Source type. In this case
a directory can be selected in the dialog after pressing Browse.With the
 Database source type you can select an
existing database connection or create one to the selected database type.
Available database types are
Database source type you can select an
existing database connection or create one to the selected database type.
Available database types are ODBC,OGDI Vectors,Esri Personal Geodatabase,MySQLas well asPostgreSQLorMSSQL.Pressing the New button opens the Create a New OGR Database Connection dialog whose parameters are among the ones you can find in 저장된 연결 생성하기. Pressing Open you can select from the available tables for example of the PostGIS enabled database.
The last source type,
 Protocol, enables to open
data from the web using for example
Protocol, enables to open
data from the web using for example GeoJSONorCouchDBformat. After selecting the type you have to fill URI of the source.
팁
맥OS에 마운트된 외부 드라이브로부터 레이어와 프로젝트 불러오기
On macOS, portable drives that are mounted beside the primary hard drive
do not show up as expected under .
We are working on a more macOS-native open/save dialog to fix this.
As a workaround, you can type /Volumes in the File name box
and press Enter. Then you can navigate to external drives and network
mounts.
구분 텍스트 파일 가져오기¶
Delimited text file (e.g. .csv, .txt) can be loaded in QGIS
using the tools described above. However, loaded this way, it’ll show up like a
simple table data. Sometimes, delimited text files can contain geometric data
you’d want to visualize; this is what the  Add
Delimited Text Layer is designed for.
Add
Delimited Text Layer is designed for.
Click the  Open Data Source Manager icon to open the
Data Source Manager dialog and enable the
Open Data Source Manager icon to open the
Data Source Manager dialog and enable the  Delimited Text tab, as shown in figure_delimited_text.
Delimited Text tab, as shown in figure_delimited_text.
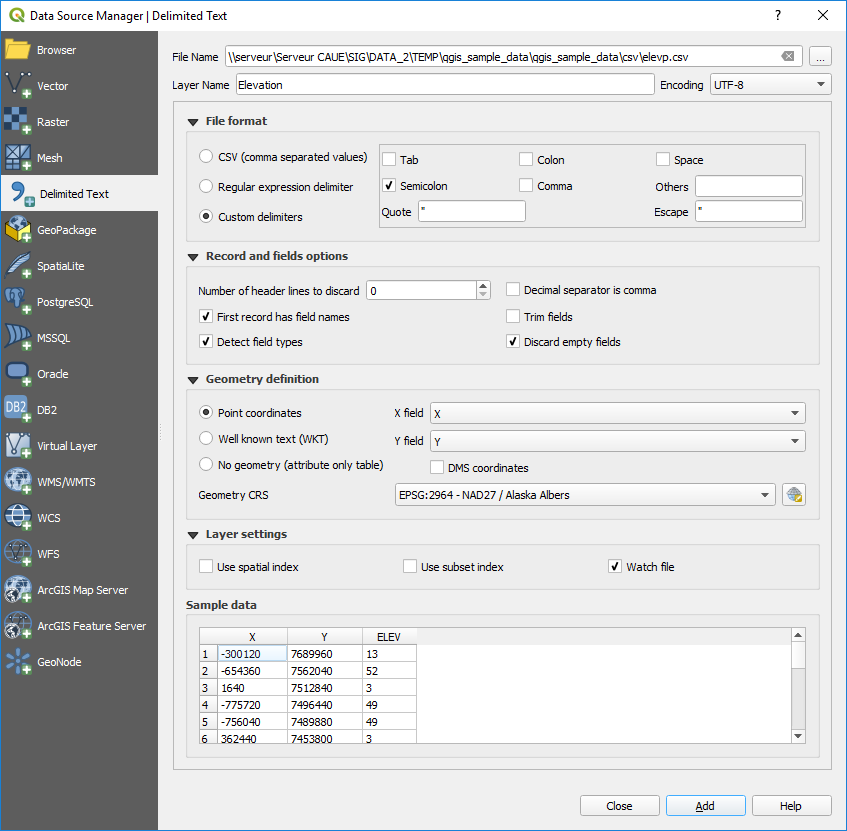
구분 텍스트 대화창¶
First, select the file to import (e.g., qgis_sample_data/csv/elevp.csv)
by clicking on the Browse button. In the Layer name field,
provide the name to use for the layer in the project (e.g., Elevation).
File format¶
Once the file is selected, QGIS attempts to parse the file with the most recently used delimiter, trying to identify fields and rows. To enable QGIS to properly parse the file, it is important to select the correct delimiter. You can specify a delimiter by activating:
Records and fields¶
Other than settings to identify rows and fields in the data, some convenient options can be used to tweak the data recognition:
Number of header lines to discard: convenient when you want to avoid some lines to show in the import, either because those are blank lines or with another formatting.
 First records has field names: values in the first row
of data are used as field names, otherwise QGIS adds a fields row of a type
First records has field names: values in the first row
of data are used as field names, otherwise QGIS adds a fields row of a type
field_1,field_2… Detect field types: automatically recognizes the field
type. If unchecked then all attributes are treated as text fields.
Detect field types: automatically recognizes the field
type. If unchecked then all attributes are treated as text fields. Decimal separator is comma: if necessary, you can force
a comma to be the decimal separator.
Decimal separator is comma: if necessary, you can force
a comma to be the decimal separator. Trim fields: allows you to trim leading and trailing
spaces from fields.
Trim fields: allows you to trim leading and trailing
spaces from fields.
As you set the parser properties, a sample data preview updates at the bottom of the dialog.
Geometry definition¶
Once the file is parsed, set Geometry definition to
 Point coordinates and provide the X
field and Y field if the layer is of point geometry type and
contain such coordinate fields. If the coordinates are defined as
degrees/minutes/seconds, activate the
Point coordinates and provide the X
field and Y field if the layer is of point geometry type and
contain such coordinate fields. If the coordinates are defined as
degrees/minutes/seconds, activate the  DMS coordinates
checkbox;
DMS coordinates
checkbox; Well known text (WKT) option if the spatial
information is represented by WKT: select the Geometry field
containing the WKT definition and choose the approriate Geometry
field or let QGIS auto-detect it;
Well known text (WKT) option if the spatial
information is represented by WKT: select the Geometry field
containing the WKT definition and choose the approriate Geometry
field or let QGIS auto-detect it;If the file contains non-spatial data, activate
 No
geometry (attribute only table) and it will be loaded as an ordinary table.
No
geometry (attribute only table) and it will be loaded as an ordinary table.
Besides the features geometry information, you can also set the layer’s
Geometry CRS using the  Select CRS widget.
Select CRS widget.
Layer settings¶
여기에 더해, 다음 옵션을 활성화시킬 수 있습니다:
 Use spatial index to improve the performance of
displaying and spatially selecting features;
Use spatial index to improve the performance of
displaying and spatially selecting features; Use subset index to improve performance of subset
filters (when defined in the layer properties);
Use subset index to improve performance of subset
filters (when defined in the layer properties); Watch file to watch for changes to the file by other
applications while QGIS is running.
Watch file to watch for changes to the file by other
applications while QGIS is running.
At the end, click OK to add the layer to the map. In our example, a
point layer named Elevation is added to the project and behaves like any
other map layer in QGIS. However, this layer is the result of a query on the
.csv source layer (hence, linked to it) and would require to be
saved in order to get a spatial layer on disk.
DXF 또는 DWG 파일 가져오기¶
DXF and DWG files can be added to QGIS by simple drag-and-drop
from the common
Browser Panel. You’ll be prompted to select the sublayers you’d like to add
to the project. Layers are added with random style properties.
참고
포인트, 라인 그리고/또는 폴리곤 같은 도형 유형을 담고 있는 DXF 파일의 경우, <filename.dxf> entities <geometry type> 을 따와서 레이어를 명명합니다.
To keep the dxf/dwg file structure and its symbology in QGIS, you may want to use the dedicated tool which allows you to:
import elements from the drawing file into a GeoPackage database.
and add to the project any of the imported elements.
In the DWG/DXF Import dialog, to first import the drawing file contents:
Input the location of the Target package, i.e. the new GeoPackage file that will store the data. If an existing file is provided, then it will be overwritten.
Specify the coordinate reference system of the data in the drawing file.
Check
 Expand block references to import the
blocks in the drawing file as normal elements.
Expand block references to import the
blocks in the drawing file as normal elements.Check
 Use curves to promote the imported layers
to a
Use curves to promote the imported layers
to a curvedgeometry type.Use the Import button to select the DWG/DXF file to use (one per geopackage). The GeoPackage database will be automatically populated with the drawing file content. Depending on the size of the *CAD file, this could take some time.
After the .dwg or .dxf data is imported into the GeoPackage
database the frame in the lower half of the dialog is populated with the list of
layers from the imported file. There you can select which layers to add to the
QGIS project:
At the top, set a Group name to group the drawing files in the project.
Check layers to show: Each selected layer is added to an ad hoc group which contains vector layers for the point, line, label and area features of the drawing layer. The style of each layer is setup so that it resembles the look it originally had in *CAD.
Check whether layer should be visible at opening.
Alternatively using the
 Merge layers option places all
layers in a single group.
Merge layers option places all
layers in a single group.Press OK to open the layers in QGIS.
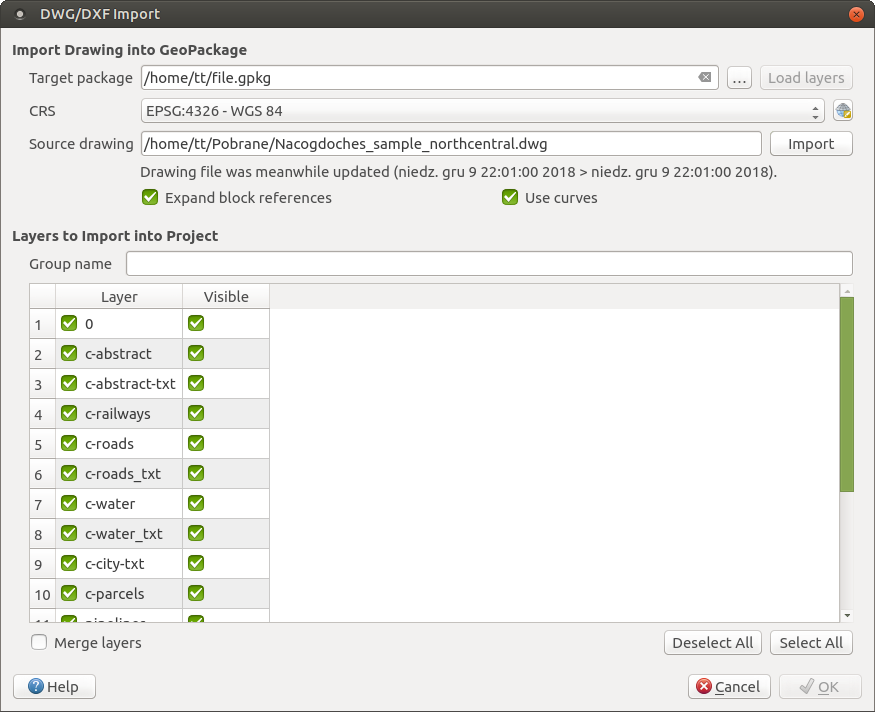
Import dialog for DWG/DXF files¶
OpenStreetMap 벡터 가져오기¶
최근 몇 년 동안, OpenStreetMap 프로젝트가 인기를 끌고 있습니다. 많은 나라에서 디지털 도로 지도 같은 무료로 쓸 수 있는 지리 데이터가 없기 때문입니다. GPS 데이터, 항공사진 또는 현지인의 지식으로부터 편집 가능하고 무료인 세계 지도를 생성하는 것이 OSM(OpenStreetMap) 프로젝트의 목표입니다. 이 목표를 돕기 위해, QGIS는 OSM 데이터를 지원하고 있습니다.
Browser Panel 을 통해 맵 캔버스에 .osm 파일을 불러올 수 있는데, 이때 도형 유형을 바탕으로 하위 레이어를 선택할 수 있는 대화창이 열립니다. 불러온 레이어는 파일에 있는 모든 도형 유형 데이터를 담고 있으며 .osm 파일 데이터 구조를 유지할 것입니다.
SpatiaLite 레이어¶
 처음으로 SpatiaLite 데이터베이스에서 데이터를 불러오는 경우, 다음 가운데 한 방법으로 시작하십시오:
처음으로 SpatiaLite 데이터베이스에서 데이터를 불러오는 경우, 다음 가운데 한 방법으로 시작하십시오:
This will bring up a window that will allow you either to connect to a
SpatiaLite database already known to QGIS, which you can choose from the
drop-down menu, or to define a new connection to a new database. To define a
new connection, click on New and use the file browser to point to
your SpatiaLite database, which is a file with a .sqlite extension.
QGIS는 SpatiaLite에서 편집할 수 있는 뷰도 지원합니다.
GRASS¶
GRASS GIS 통합 에서 GRASS 벡터 데이터 작업을 설명하고 있습니다.
QGIS 사용자 지정 포맷¶
QGIS는 특화된 불러오기 도구를 이용해 응용 프로그램에 불러올 수 있는 사용자 지정 포맷을 2개 제공합니다.
임시 스크래치 레이어(Temporary Scratch Layer): 함께 열린 프로젝트에 종속된 메모리 레이어 (자세한 내용은 새 임시 스크래치 레이어 생성하기 참조)
가상 레이어(Virtual Layer): 다른 레이어(들)에 대한 쿼리에서 산출된 레이어 (자세한 내용은 Creating virtual layers 참조)
QLR - QGIS Layer Definition File¶
Layer definitions can be saved as a
Layer Definition File (QLR -
.qlr) using
in the layer
context menu.
The QLR format makes it possible to share 《complete》 QGIS layers with other QGIS users. QLR files contain links to the data sources and all the QGIS style information necessary to style the layer.
QLR files are shown in the Browser Panel and can be used to add layers (with their saved styles) to the Layers Panel. You can also drag and drop QLR files from the system file manager into the map canvas.
웹 서비스를 연결하기¶
QGIS를 통해 서로 다른 OGC 웹 서비스 유형(WM(T)S, WFS(-T), CSW 등등)에 접근할 수 있습니다. QGIS 서버 덕분에, 이 서비스들을 웹 상에 공개할 수도 있습니다. OGC 데이터 작업 에서 이런 역량 및 방법에 대해 설명하고 있습니다.