QGIS GUI¶
When QGIS starts, a GUI displays as shown in the figure below (the numbers 1 through 5 in yellow circles are discussed below).
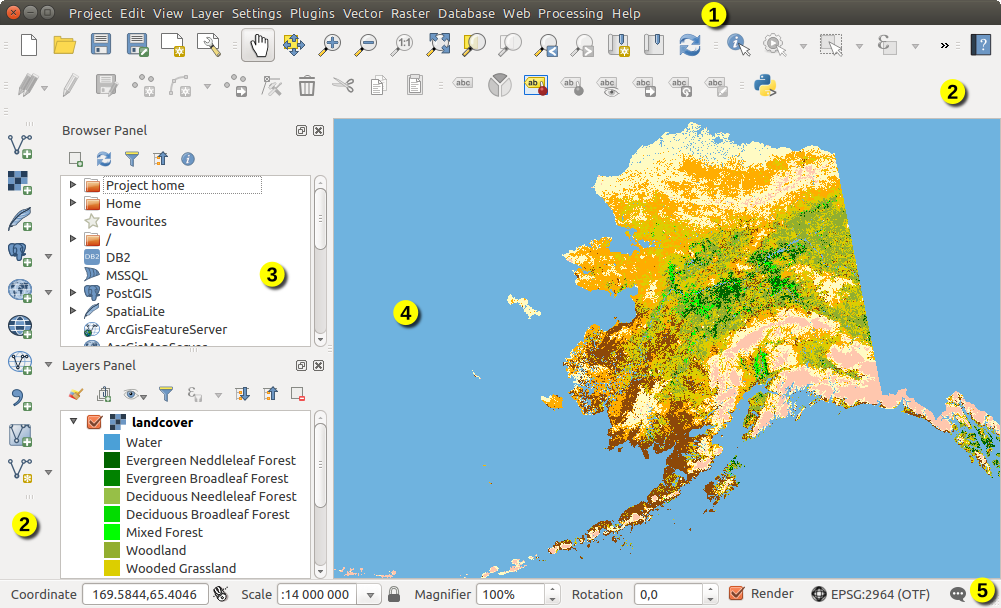
알래스카 샘플 데이터를 불러온 QGIS GUI¶
참고
사용자의 운영체제 및 창 관리자에 따라 창 양식(제목 바 등등)이 다르게 나타날 수도 있습니다.
QGIS GUI를 다음 5개의 요소로 구분할 수 있습니다:
메뉴 바
툴바
패널
맵 뷰
상태 바
Scroll down for detailed explanations of these features.
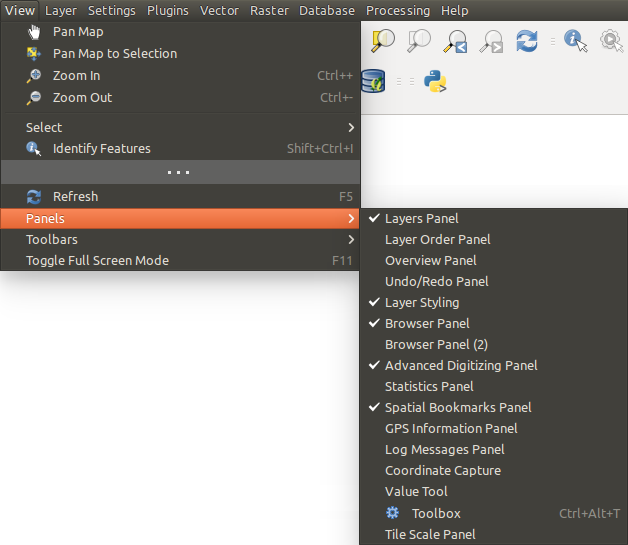
패널 및 툴바¶
From the menu (or  ), you can
switch QGIS widgets () and toolbars
() on and off. To (de)activate any of them,
right-click the menu bar or toolbar and choose the item you want.
Each panel or toolbar can be moved and placed wherever you feel comfortable
within the QGIS interface.
The list can also be extended with the activation of Core or external
plugins.
), you can
switch QGIS widgets () and toolbars
() on and off. To (de)activate any of them,
right-click the menu bar or toolbar and choose the item you want.
Each panel or toolbar can be moved and placed wherever you feel comfortable
within the QGIS interface.
The list can also be extended with the activation of Core or external
plugins.
툴바¶
The toolbar provides access to most of the same functions as the menus, plus additional tools for interacting with the map. Each toolbar item has pop-up help available. Hover your mouse over the item and a short description of the tool’s purpose will be displayed.
사용자의 필요에 따라 모든 툴바를 이동할 수 있습니다. 또, 오른쪽 클릭으로 컨텍스트 메뉴를 불러오거나 툴바 위에 마우스를 가져 가서 툴바를 꺼버릴 수도 있습니다.
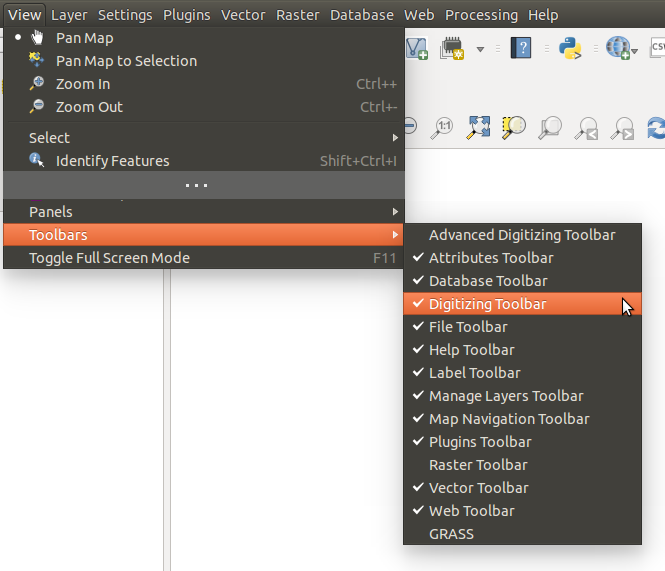
툴바 메뉴¶
팁
툴바를 복구하기
사용자가 실수로 툴바를 꺼버렸을 경우, 메뉴 옵션을 (또는  를) 선택해서 다시 불러올 수 있습니다. 어떤 이유로 인터페이스에서 툴바가 (또는 다른 위젯이) 완전히 사라졌을 경우, 초기 GUI 복구 를 보시면 복구에 필오한 팁을 얻으실 수 잇습니다.
를) 선택해서 다시 불러올 수 있습니다. 어떤 이유로 인터페이스에서 툴바가 (또는 다른 위젯이) 완전히 사라졌을 경우, 초기 GUI 복구 를 보시면 복구에 필오한 팁을 얻으실 수 잇습니다.
맵 뷰¶
맵 캔버스 라고도 불리는 이 창은 QGIS의 《총화》입니다. 이 영역에 맵을 표시하기 때문이죠. 이 창에 표시되는 맵은 사용자가 선택해서 불러온 벡터 및 래스터 레이어에 따라 달라집니다.
When you add a layer (see e.g. 데이터 열기), QGIS automatically looks for its Coordinate Reference System (CRS) and zooms to its extent if you start with a blank QGIS project. The layer’s CRS is then applied to the project. If there are already layers in the project, and if the new layer has the same CRS as the project, its features falling in the current map canvas extent will be visualized. If the new layer is in a different CRS from the project’s, you must Enable on-the-fly CRS transformation from the (see On The Fly (OTF) CRS Transformation). The added layer should now be visible if data are available in the current view extent.
The map view can be panned, shifting the display to another region of the map, and it can be zoomed in and out. Various other operations can be performed on the map as described in the 툴바 section. The map view and the legend are tightly bound to each other — the maps in the view reflect changes you make in the legend area.
팁
마우스 휠로 맵을 확대/축소
마우스 휠을 이용해서 맵을 확대하거나 축소할 수 있습니다. 맵 영역 안쪽에 마우스 커서를 가져간 다음 휠을 앞으로 (사용자에게서 멀리) 돌리면 확대되고 뒤로 (사용자쪽으로) 돌리면 축소됩니다. 이 때 마우스 커서 위치를 중심으로 확대/축소됩니다. 메뉴의 Map tools 탭에서 마우스 휠 확대/축소 방식을 사용자 지정할 수 있습니다.
팁
방향 키와 스페이스 바로 맵을 이동
You can use the arrow keys to pan the map. Place the mouse cursor inside the map area and click on the arrow keys to pan left, right, up and down. You can also pan the map by moving the mouse while holding down the space bar or the middle mouse button (or holding down the mouse wheel).
3D Map View¶
3D visualization support is offered through the 3D map view.
참고
3D visualization in QGIS requires a recent version of the QT library (5.8 or later).
You create and open a 3D map view via  .
A floating QGIS panel will appear. The panel can be docked.
.
A floating QGIS panel will appear. The panel can be docked.
To begin with, the 3D map view has the same extent and view as the 2D canvas. There is no dedicated toolbar for navigation in the 3D canvas. You zoom in/out and pan in the same way as in the main 2D canvas. You can also zoom in and out by dragging the mouse down/up with the right mouse button pressed.
Navigation options for exploring the map in 3D:
Tilt and rotate
To tilt the terrain (rotating it around a horizontal axis that goes through the center of the window):
Drag the mouse forward/backward with the middle mouse button pressed
Press Shift and drag the mouse forward/backward with the left mouse button pressed
Press Shift and use the up/down keys
To rotate the terrain (around a vertical axis that goes through the center of the window):
Drag the mouse right/left with the middle mouse button pressed
Press Shift and drag the mouse right/left with the left mouse button pressed
Press Shift and use the left/right keys
Change the camera angle
Pressing Ctrl and dragging the mouse with the left mouse button pressed changes the camera angle corresponding to directions of dragging
Pressing Ctrl and using the arrow keys turns the camera up, down, left and right
Move the camera up/down
Pressing the Page Up/Page Down keys moves the terrain up and down, respectively
Zoom in and out
Dragging the mouse with the right mouse button pressed will zoom in (drag down) and out (drag up)
Move the terrain around
Dragging the mouse with the left mouse button pressed moves the terrain around
Using the up/down/left/right keys moves the terrain closer, away, right and left, respectively
To reset the camera view, click the  Zoom Full
button on the top of the 3D canvas panel.
Zoom Full
button on the top of the 3D canvas panel.
Terrain Configuration¶
A terrain raster provides the elevation. This raster layer must contain a band that represents elevation. To select the terrain raster:
Click the
 Configure… button at the top of
the 3D canvas panel to open the 3D configuration window
Configure… button at the top of
the 3D canvas panel to open the 3D configuration windowChoose the terrain raster layer in the Elevation pull-down menu
In the 3D Configuration window there are various other options to fine-tune the 3D scene. Before diving into the details, it is worth noting that terrain in a 3D view is represented by a hierarchy of terrain tiles and as the camera moves closer to the terrain, existing tiles that do not have sufficient detail are replaced by smaller tiles with more details. Each tile has mesh geometry derived from the elevation raster layer and texture from 2D map layers.
Configuration options and their meaning:
Elevation: Raster to be used for generation of terrain.
Vertical scale: Scale factor for vertical axis. Increasing the scale will exaggerate the terrain.
Tile resolution: How many samples from the terrain raster layer to use for each tile. A value of 16px means that the geometry of each tile will be built from 16x16 elevation samples. Higher numbers create more detailed terrain tiles at the expense of increased rendering complexity.
Skirt height: Sometimes it is possible to see small cracks between tiles of the terrain. Raising this value will add vertical walls (《skirts》) around terrain tiles to hide the cracks.
Map tile resolution: Width and height of the 2D map images used as textures for the terrain tiles. 256px means that each tile will be rendered into an image of 256x256 pixels. Higher numbers create more detailed terrain tiles at the expense of increased rendering complexity.
Max. screen error: Determines the threshold for swapping terrain tiles with more detailed ones (and vice versa) - i.e. how soon the 3D view will use higher quality tiles. Lower numbers mean more details in the scene at the expense of increased rendering complexity.
Max. ground error: The resolution of the terrain tiles at which dividing tiles into more detailed ones will stop (splitting them would not introduce any extra detail anyway). This value limits the depth of the hierarchy of tiles: lower values make the hierarchy deep, increasing rendering complexity.
Zoom labels: Shows the number of zoom levels (depends on the map tile resolution and max. ground error).
 Show map tile info: Include border and tile numbers for the
terrain tiles (useful for troubleshooting terrain issues)
Show map tile info: Include border and tile numbers for the
terrain tiles (useful for troubleshooting terrain issues) Show bounding boxes: Show 3D bounding boxes of the terrain
tiles (useful for troubleshooting terrain issues)
Show bounding boxes: Show 3D bounding boxes of the terrain
tiles (useful for troubleshooting terrain issues)
3D vector layers¶
A vector layer with elevation values can be shown in the 3D map view by checking Enable 3D Renderer in the 3D View section of the vector layer properties. A number of options are available for controlling the rendering of the 3D vector layer.
상태 바¶
The status bar provides you with general information about the map view and processed or available actions, and offers you tools to manage the map view.
On the left side of the status bar, the locator bar, a quick search widget,
helps you find and run any feature or options in QGIS. Simply type text
associated with the item you are looking for (name, tag, keyword…) and you get
a list that updates as you write. You can also limit the search scope using
locator filters. Click the  button to
select any of them and press the Configure entry for global settings.
button to
select any of them and press the Configure entry for global settings.
In the area next to the locator bar, a summary of actions you’ve carried out will be shown when needed (such as selecting features in a layer, removing layer) or a long description of the tool you are hovering over (not available for all tools).
In case of lengthy operations, such as gathering of statistics in raster layers, executing Processing algorithms or rendering several layers in the map view, a progress bar is displayed in the status bar.
The ![]() Coordinate option shows the current position of the mouse,
following it while moving across the map view. You can set the units (and precision)
in the tab.
Click on the small button at the left of the textbox to toggle between
the Coordinate option and the
Coordinate option shows the current position of the mouse,
following it while moving across the map view. You can set the units (and precision)
in the tab.
Click on the small button at the left of the textbox to toggle between
the Coordinate option and the  Extents option that displays
the coordinates of the current bottom-left and top-right
corners of the map view in map units.
Extents option that displays
the coordinates of the current bottom-left and top-right
corners of the map view in map units.
Next to the coordinate display you will find the Scale display. It shows the scale of the map view. There is a scale selector, which allows you to choose between predefined and custom scales.
On the right side of the scale display, press the  button to lock
the scale to use the magnifier to zoom in or out. The magnifier allows you to zoom
in to a map without altering the map scale, making it easier to tweak the
positions of labels and symbols accurately. The magnification level is expressed as a
percentage. If the Magnifier has a level of 100%, then the current
map is not magnified. Additionally, a default magnification value can be defined
within ,
which is very useful for high-resolution screens to enlarge small symbols.
button to lock
the scale to use the magnifier to zoom in or out. The magnifier allows you to zoom
in to a map without altering the map scale, making it easier to tweak the
positions of labels and symbols accurately. The magnification level is expressed as a
percentage. If the Magnifier has a level of 100%, then the current
map is not magnified. Additionally, a default magnification value can be defined
within ,
which is very useful for high-resolution screens to enlarge small symbols.
확대경(Magnifier) 오른쪽에서 맵 뷰의 시계 방향 회전량(rotation)을 도(|degrees|) 단위로 정의할 수 있습니다.
On the right side of the status bar, there is a small checkbox which can be used temporarily to prevent layers being rendered to the map view (see section 렌더링 작업).
To the right of the render functions, you find the ![]() EPSG:code button showing the current project CRS. Clicking on
this opens the Project Properties dialog and lets you apply another
CRS to the map view.
EPSG:code button showing the current project CRS. Clicking on
this opens the Project Properties dialog and lets you apply another
CRS to the map view.
The  Messages button next to it opens the Log
Messages Panel which has information on underlying processes (QGIS startup, plugins
loading, processing tools…)
Messages button next to it opens the Log
Messages Panel which has information on underlying processes (QGIS startup, plugins
loading, processing tools…)
Depending on the Plugin Manager settings, the status
bar can sometimes show icons to the right to inform you about availability
of  new or
new or  upgradeable plugins. Click the icon to
open the Plugin Manager dialog.
upgradeable plugins. Click the icon to
open the Plugin Manager dialog.
팁
사용자 맵 캔버스의 정확한 축척을 계산하기
When you start QGIS, the default CRS is WGS 84 (EPSG 4326) and
units are degrees. This means that QGIS will interpret any
coordinate in your layer as specified in degrees. To get correct scale values,
you can either manually change this setting in the General
tab under (e.g. to meters), or you can use
the ![]() EPSG:code icon seen above. In the latter case,
the units are set to what the project projection specifies (e.g.,
EPSG:code icon seen above. In the latter case,
the units are set to what the project projection specifies (e.g., +units=us-ft).
메뉴 옵션에서 실행 시 기본적으로 적용할 좌표계를 설정할 수 있다는 사실을 알아두십시오.