IGU QGIS¶
When QGIS starts, you are presented with the GUI as shown in the figure (the numbers 1 through 5 in yellow circles are discussed below).
Figure QGIS GUI 1:
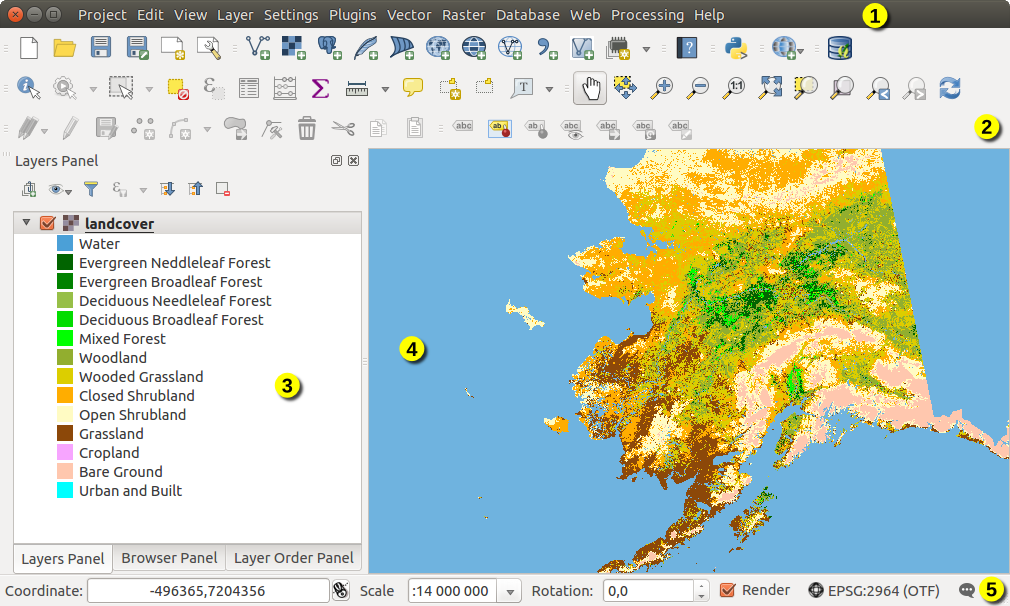
QGIS GUI with Alaska sample data
Nota
Las decoraciones de las ventanas (barra de título, etc.) pueden ser distintas dependiendo de su sistema operativo y su gestor de ventanas.
The QGIS GUI is divided into five areas:
Barra de Menú
Barras de herramientas
Paneles
Vista del mapa
Barra de Estado
These five components of the QGIS interface are described in more detail in the following sections. Two more sections present keyboard shortcuts and context help.
Paneles y Barras de Herramientas¶
From the View menu (Settings under KDE), you can switch on and off QGIS widgets (Panels ‣) or toolbars (Toolbars ‣). You can (de)activate any of them by right-clicking the menu bar or a toolbar and choose the item you want. Each panel or toolbar can be moved and placed wherever you feel comfortable with in QGIS interface. The list can also be extended with the activation of Core or external plugins.
Barras de herramientas¶
La barra de herramientas proporciona acceso a la mayoría de las mismas funciones como las de los menús, y herramientas adicionales para interactuar con el mapa. Cada elemento de la barra de herramientas tiene ayuda emergente disponible. Mantenga el puntero del ratón sobre el elemento y una breve descripción del propósito de la herramienta se mostrará.
Every toolbar can be moved around according to your needs. Additionally, they can be switched off using the right mouse button context menu, or by holding the mouse over the toolbars.
Figure Toolbars:
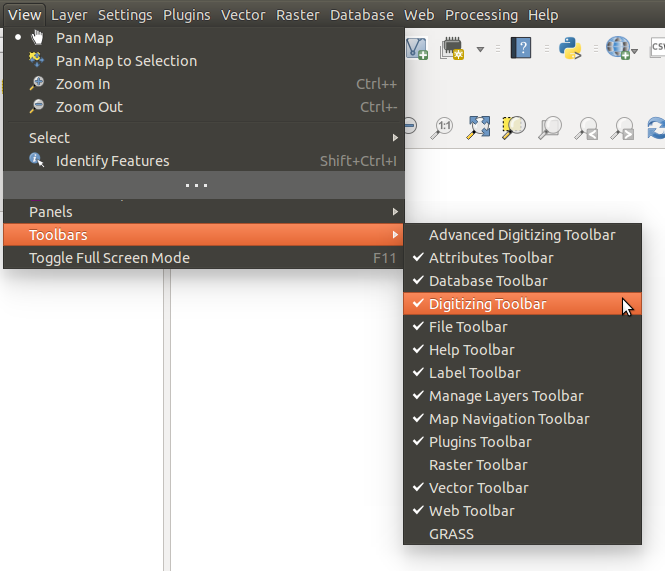
The Toolbars menu
Truco
Restauración de barras de herramientas
If you have accidentally hidden a toolbar, you can get it back by choosing menu option View ‣ Toolbars ‣ (or Settings ‣ Toolbars ‣ under Linux KDE). If for some reason a toolbar (or any other widget) totally disappears from the interface, you’ll find tips to get it back at restoring initial GUI.
Paneles¶
QGIS provides by default many panels to work with.
Figure Panels:
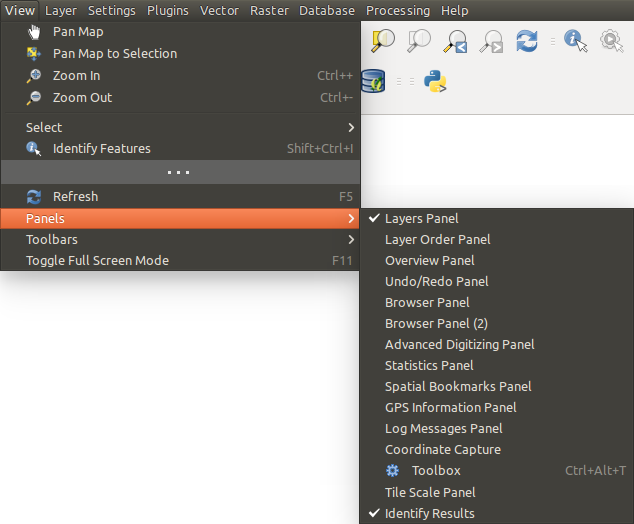
El menú de paneles
Some of these panels are described below while others may be found in different parts of the document, namely:
- the Browser Panel
- the Advanced Digitizing Panel
- the Spatial Bookmarks Panel
- the GPS Information Panel
- the Tile Scale Panel
- the Identify Panel
- the User Input Panel
Panel de Capas¶
The layers panel lists all the layers in the project. The checkbox in each legend entry can be used to show or hide the layer. The toolbar in the layers panel allows you to:
 Add new group
Add new group Manage Visibility: control visibility of layers and
preset layers combination
Manage Visibility: control visibility of layers and
preset layers combination Filter Legend by Map Content: only the layers that are set
visible and whose features intersect the current map canvas have their style
rendered in the layers panel. Otherwise, a generic NULL symbol is applied to the
layer. Based on the layer symbology, this is a convenient way to identify which
kind of features from which layers cover your area of interest.
Filter Legend by Map Content: only the layers that are set
visible and whose features intersect the current map canvas have their style
rendered in the layers panel. Otherwise, a generic NULL symbol is applied to the
layer. Based on the layer symbology, this is a convenient way to identify which
kind of features from which layers cover your area of interest. Filter Legend by Expression: helps you apply an
expression to remove from the selected layer tree styles that have no feature
satisfying the condition. This can be used for example to highlight features that are
within a given area/feature of another layer.
From the drop-down list, you can edit and clear the expression set.
Filter Legend by Expression: helps you apply an
expression to remove from the selected layer tree styles that have no feature
satisfying the condition. This can be used for example to highlight features that are
within a given area/feature of another layer.
From the drop-down list, you can edit and clear the expression set. Expand All or
Expand All or  Collapse All
layers and groups in the layers panel.
Collapse All
layers and groups in the layers panel.- and
 Remove Layer/Group currently selected.
Remove Layer/Group currently selected.
Figure Layer tools Bar:

Layer Toolbar in Layers Panel
The button  allows you to add Presets views in the legend.
Presets are a way to save and easily restore a combination of layers with their
current style. To add a preset view, just set visible the layers you want, with
their desired symbology, and click on
allows you to add Presets views in the legend.
Presets are a way to save and easily restore a combination of layers with their
current style. To add a preset view, just set visible the layers you want, with
their desired symbology, and click on  button.
Choose Add Preset... from the drop-down menu and give a name to the preset.
The added preset is listed at the bottom of the drop-down menu and is recalled by
clicking on it.
button.
Choose Add Preset... from the drop-down menu and give a name to the preset.
The added preset is listed at the bottom of the drop-down menu and is recalled by
clicking on it.
The Replace Preset ‣ option helps you overwrite a preset content with the current map view while the Remove Current Preset button deletes the active preset.
Todos los preestablecidos añadidos están presentes en el diseño de impresión con el fin de permitirle crear un diseño de mapa en base a sus puntos de vista específicos (ver Main properties).
Nota
Tools to manage the layers panel are also available to layout the map and legend items of the print composer
Una capa se puede seleccionar y arrastrar hacia arriba o hacia abajo en la leyenda para cambiar el orden. El orden-z significa que las capas enlistadas más cerca de la parte superior de la leyenda son dibujadas sobre las capas que figuran más abajo en la leyenda.
Nota
This behavior can be overridden by the Layer Order panel.
Layers in the legend window can be organized into groups. There are two ways to do this:
- Press the
 icon to add a new group. Type in a name for
the group and press Enter. Now click on an existing layer and
drag it onto the group.
icon to add a new group. Type in a name for
the group and press Enter. Now click on an existing layer and
drag it onto the group. Seleccionar algunas capas, al hacer clic derecho en la ventana de la leyenda y elegir Grupo Seleccionado. Las capas seleccionadas serán colocadas automáticamente en un nuevo grupo.
Para llevar una capa fuera de un grupo, puede arrastrar hacia afuera , o haga clic derecho sobre él y elija Subir elemento al nivel superior.
La casilla de verificación para un grupo mostrará u ocultará todas las capas en el grupo al hacer clic.
El contenido del menú contextual del botón derecho depende si el elemento de leyenda seleccionada es un ráster o una capa vectorial. Para las capas vectoriales de GRASS ,  Botón de edición no está disponible. Vea la sección Digitalizar y editar una capa vectorial GRASS para obtener información sobre la edición de capas vectoriales de GRASS.
Botón de edición no está disponible. Vea la sección Digitalizar y editar una capa vectorial GRASS para obtener información sobre la edición de capas vectoriales de GRASS.
Below are listed available options in context menu depending on the selected item.
Enabling the Mutually Exclusive Group option you can make a group have only one layer visible at the same time. Whenever a layer within the group is set visible the others will be toggled not visible.
Es posible seleccionar mas de una capa o grupo al mismo tiempo manteniendo presionada la tecla Ctrl mientras selecciona las capas con el botón izquierdo del ratón. Después puede mover todas las capas a un nuevo grupo al mismo tiempo.
You may also delete more than one layer or group at once by selecting several items with the Ctrl key and pressing Ctrl+D afterwards. This way, all selected layers or groups will be removed from the layers list.
Editing vector layer style¶
From the Layers panel, you have shortcuts to easily and quickly edit the layer rendering. Right-click on a vector layer and select Styles –> in the list in order to:
- see the currently applied styles to the layer. In case you defined many styles for the layer, you can switch from one to another and have your layer rendering automatically updated in the map canvas.
- copy the current style, and when applicable, paste a copied style from another layer
- rename the current style, add a new one (which is actually a copy of the current one) or delete the current style (when multiple styles available).
Nota
The previous options are also available for raster layer.
Whether the features in the vector layer have all the same unique symbol or they are classified (in that case, the layer is displayed in a tree structure with each class as sub-item), the following options are available at layer level or class level:
- a Edit Symbol... button to open the El Selector de Símbolo dialog and update any property (symbol, size, color...) of the layer or feature symbol. Double-clicking on a feature does also open the Symbol Selector dialog.
- a Selector de color widget with a Color Wheel from which you can click a color and have it automatically update the symbol fill color. For convenience, Recent colors are available at the bottom of the color wheel.
- a
 Show All Items and
Show All Items and  Hide All
Items to toggle on or off the visibility of all the classes of features. This avoids
(un)checking items one by one.
Hide All
Items to toggle on or off the visibility of all the classes of features. This avoids
(un)checking items one by one.
Truco
Quickly share a layer style
From the context menu, copy the style of a layer and paste it to a group or a selection of layers: the style is applied to all the layers that are of the same type (vector vs raster) as the original layer and, in case of vector, have the same geometry type (point, line or polygon).
Trabajar con el orden de la leyenda de la capa independiente¶
There is a panel that allows you to define an independent drawing order for
the layers panel. You can activate it in the menu
Settings ‣ Panels ‣ Layer Order Panel. This feature allows you
to, for instance, order your layers in order of importance, but still display
them in the correct order (see figure_layer_order). Checking the  Control rendering order box underneath the list of layers will
cause a revert to default behavior.
Control rendering order box underneath the list of layers will
cause a revert to default behavior.
Figure Layer Order:
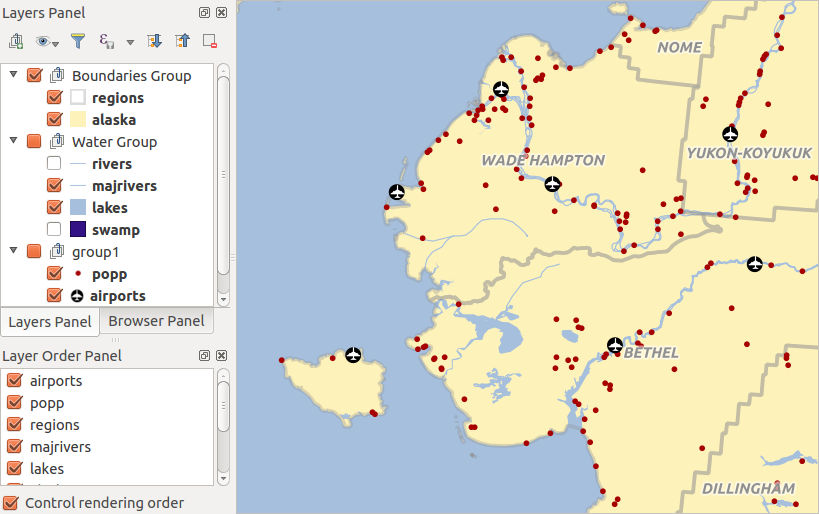
Definir el orden de la leyenda de una capa independiente
Panel resumen estadístico¶
This panel can show some statistics on a specific vector layers. The panel allows users to choose:
- the vector layer;
- the column or the expression;
- filter statistics to selected features;
Actualizar las informaciones;
- the statistics information to display with the bottom right button;
Panel de vista general de QGIS¶
In QGIS, you can use an overview panel that provides a full extent view of layers added to it. Within the view is a rectangle showing the current map extent. This allows you to quickly determine which area of the map you are currently viewing. Note that labels are not rendered to the map overview even if the layers in the map overview have been set up for labelling. If you click and drag the red rectangle in the overview that shows your current extent, the main map view will update accordingly.
Panel de mensajes del registro¶
When loading or processing some operations, you can track and follow messages
that appear in different tabs using the  Log Messages Panel.
It can be activated using the most right icon in the bottom status bar.
Log Messages Panel.
It can be activated using the most right icon in the bottom status bar.
Panel deshacer/rehacer¶
For each layer being edited, this panel shows the list of actions done, allowing to quickly undo a set of actions by simply selecting the action listed above.
Vista del mapa¶
También llamado Vista del mapa,este es el “final del negocio” de QGIS — ¡los mapas son desplegados en esta zona! El mapa que se muestra en esta ventana dependerá de las capas vectoriales y ráster que ha elegido cargar (ver secciones siguientes para obtener más información sobre cómo cargar capas). La vista del mapa se puede desplazar, cambiar el enfoque de la pantalla del mapa a otra región, y que se puede hacer zum dentro y fuera. Varias otras operaciones se pueden realizar en el mapa como esta descrito en la descripción de la barra de herramientas anteriormente. La vista del mapa y la leyenda están estrechamente vinculados entre sí — los mapas en vista reflejan los cambios que realice en el área de leyenda .
Truco
Zum al mapa con la rueda del ratón
Puede utilizar la rueda del ratón para acercar y alejar zum en el mapa. Coloque el cursor del ratón dentro del mapa y gire la rueda hacia adelante (hacia la derecha) para acercar y hacia atrás (hacia usted) para alejarlo. El zum se centra en la posición del cursor del ratón. Puede personalizar el comportamiento del zum de la rueda del ratón usando la pestaña Herramientas del mapa bajo el menú Configuración‣ Opciones
Truco
Desplazar el mapa con las teclas de dirección y barra de espaciadora
Puede utilizar las teclas de flechas para desplazar el mapa. Coloque el cursor dentro del mapa y haga clic en la tecla de flecha a la derecha para desplazarse al este, tecla de flecha izquierda para el oeste, flecha arriba para el norte y flecha abajo al sur. Puede también desplazar el mapa utilizando la barra espaciadora o al hacer clic en la rueda del ratón: basta con mover el ratón mientras mantiene pulsada la barra espaciadora o haga clic en la rueda del ratón.
Barra de Estado¶
The status bar provides you with general information about the map view, and actions processed or available and offers you tools to manage the map view.
On the left side of the status bar, you can get a summary of actions you’ve done (such as selecting features in a layer, removing layer) or a long description of the tool you are hovering over (not available for all tools). On startup, the bar status also informs you about availability of new or upgradeable plugins (if checked in Plugin Manager settings).
In case of lengthy operations, such as gathering of statistics in raster layers or rendering several layers in map view, a progress bar is displayed in the status bar to show the current progress of the action.
The ![]() Coordinate option shows the current position of the mouse,
following it while moving across the map view. You can set the unit (and precision)
to use in the project properties, General tab.
Click on the small button at the left of the textbox to toggle between
the Coordinate option and the
Coordinate option shows the current position of the mouse,
following it while moving across the map view. You can set the unit (and precision)
to use in the project properties, General tab.
Click on the small button at the left of the textbox to toggle between
the Coordinate option and the  Extents option that displays
in map units, the coordinates of the current lower leftmost and upper rightmost
points of the map view, as you pan and zoom in and out.
Extents option that displays
in map units, the coordinates of the current lower leftmost and upper rightmost
points of the map view, as you pan and zoom in and out.
Next to the coordinate display you will find the Scale display. It shows the scale of the map view. If you zoom in or out, QGIS shows you the current scale. There is a scale selector, which allows you to choose among predefined and custom scales to assign to the map view.
A la derecha de la escala desplegada se puede definir una rotación horaria actual de su vista de mapa en grados.
On the right side of the status bar, there is a small checkbox which can be used to temporarily prevent layers being rendered to the map view (see section Renderizado).
To the right of the render functions, you find the ![]() Current CRS: icon with the EPSG code of the current
project CRS. Clicking on this lets you Enable ‘on the fly’ CRS
transformation properties for the current project and apply another CRS to the
map view.
Current CRS: icon with the EPSG code of the current
project CRS. Clicking on this lets you Enable ‘on the fly’ CRS
transformation properties for the current project and apply another CRS to the
map view.
Finally, the  Messages button opens the Log
Messages Panel which informs you on underlying process (QGIS startup, plugins
loading, processing tools...)
Messages button opens the Log
Messages Panel which informs you on underlying process (QGIS startup, plugins
loading, processing tools...)
Truco
Calcular la escala correcta de su lienzo de mapa
When you start QGIS, the default CRS is WGS 84 (epsg 4326) and
units are degrees. This means that QGIS will interpret any
coordinate in your layer as specified in degrees. To get correct scale values,
you can either manually change this setting, e.g. to meters, in the General
tab under Project ‣ Project Properties, or you can use
the ![]() Current CRS: icon seen above. In the latter case,
the units are set to what the project projection specifies (e.g., +units=us-ft).
Current CRS: icon seen above. In the latter case,
the units are set to what the project projection specifies (e.g., +units=us-ft).
Note that CRS choice on startup can be set in Settings ‣ Options ‣ CRS.







 Exit QGIS
Exit QGIS