Análisis raster¶
Calculadora Ráster¶
La en el menú permite realizar cálculos sobre la base de valores de píxeles de un ráster existente (vea figure_raster). Los resultados están escritos en una nueva capa ráster con un formato GDAL- reconocido.
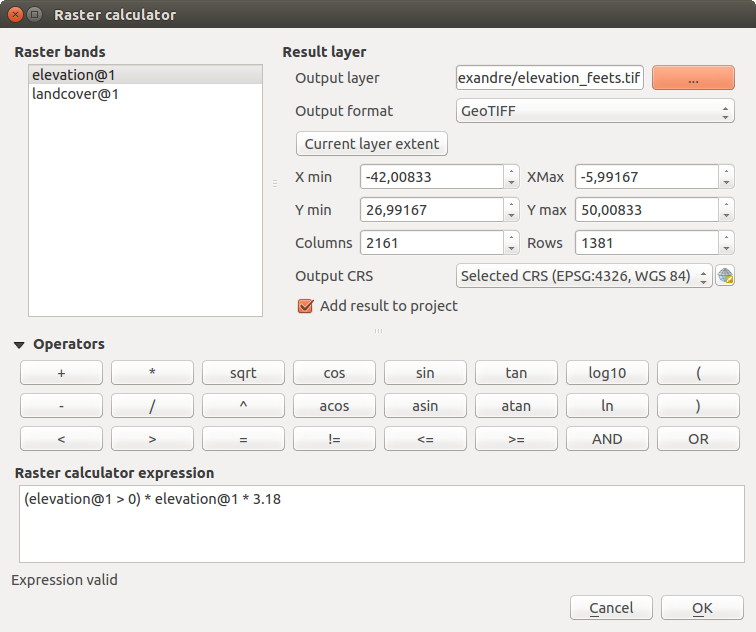
Calculadora Ráster¶
The Raster bands list contains all loaded raster layers that can be used. To add a raster to the raster calculator expression field, double click its name in the Fields list. You can then use the operators to construct calculation expressions, or you can just type them into the box.
In the Result layer section, you will need to define an output layer. You can then define the extent of the calculation area based on an input raster layer, or based on X,Y coordinates and on columns and rows, to set the resolution of the output layer. If the input layer has a different resolution, the values will be resampled with the nearest neighbor algorithm.
The Operators section contains all available operators. To add an operator
to the raster calculator expression box, click the appropriate button. Mathematical
calculations (+, -, *, … ) and trigonometric functions (sin,
cos, tan, … ) are available. Conditional expressions (=, !=,
<, >=, … ) return either 0 for false or 1 for true, and therefore can be
used with other operators and functions. Stay tuned for more operators to come!
With the  Add result to project checkbox, the result layer
will automatically be added to the legend area and can be visualized.
Add result to project checkbox, the result layer
will automatically be added to the legend area and can be visualized.
Ejemplos¶
Convert elevation values from meters to feet
Creating an elevation raster in feet from a raster in meters, you need to use the conversion factor for meters to feet: 3.28. The expression is:
"elevation@1" * 3.28
Using a mask
If you want to mask out parts of a raster – say, for instance, because you are only interested in elevations above 0 meters – you can use the following expression to create a mask and apply the result to a raster in one step.
("elevation@1" >= 0) * "elevation@1"
In other words, for every cell greater than or equal to 0 the conditional expression evaluates to 1, which keeps the original value by multiplying it by 1. Otherwise the conditional expression evaluates to 0, which sets the raster value to 0. This creates the mask on the fly.
Si desea clasificar un ráster –digamos, por ejemplo en dos clases de elevación, puede utilizar la siguiente expresión para crear un ráster con dos valores 1 y 2 en un solo paso.
("elevation@1" < 50) * 1 + ("elevation@1" >= 50) * 2
In other words, for every cell less than 50 set its value to 1. For every cell greater than or equal 50 set its value to 2.
Raster Alignment¶
This tool is able to take several rasters as input and to align them perfectly, that means:
reproyectar al mismo SRC,
remuestrea al mismo tamaño de celda y desplazamiento en la cuadrícula (grid),
clip to a region of interest,
reescale valores cuando sea necesario.
All rasters will be saved in another files.
First, open the tools from and click
on the  Add new raster button to choose one existing raster in
QGIS. Select an output file to save the raster after the alignment, the
resampling method and if the tools need to Rescale values according
to the cell size. The resampling method can be (see figure_raster_align_edit):
Add new raster button to choose one existing raster in
QGIS. Select an output file to save the raster after the alignment, the
resampling method and if the tools need to Rescale values according
to the cell size. The resampling method can be (see figure_raster_align_edit):
Vecino más próximo
Bilineal (núcleo 2x2)
Cubic (4x4 kernel): Cubic Convolution Approximation
Cubic B-Spline (4x4 kernel): Cubic B-Spline Approximation
Lanczos (6x6 kernel): Lanczos windowed sinc interpolation
Average: computes the average of all non-NODATA contributing pixels
Mode: selects the value which appears most often of all the sampled points
Maximum, Minimum, Mediane, First Quartile (Q1) or Third Quartile (Q3) of all non-NODATA contributing pixels
Nota
Methods like maximum, minimum, mediane, first and third quartiles are available only if QGIS is built with GDAL >= 2.0.

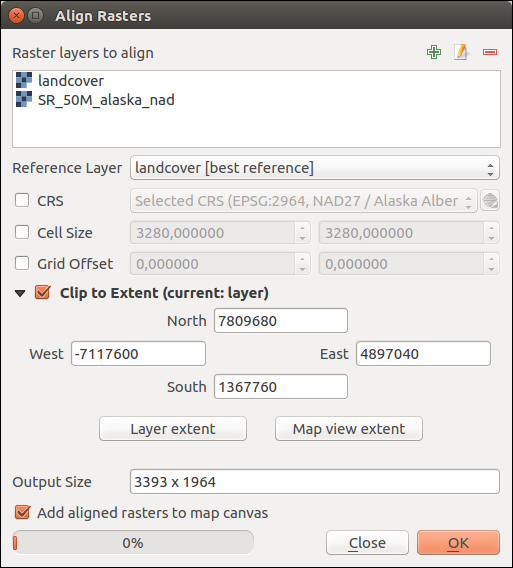
Select Raster Resampling Options¶
In the main Align raster dialog, you can still  Edit
file settings or
Edit
file settings or  Remove an existing file from the list of raster
layers. You can also choose one or more other options (see figure_raster_align):
Remove an existing file from the list of raster
layers. You can also choose one or more other options (see figure_raster_align):
Select the Reference Layer,
Transform into a new CRS,
Setup a different Cell size,
Setup a different Grid Offset,
Clip to Extent: it can be user-defined or based on a layer or the map view
Output Size,
Add aligned raster to the map canvas.
Raster Alignment¶