編集¶
QGIS は OGR, SpatiaLite, PostGIS, MSSQL SpatialやOracle Spatial vector とテーブルに対する様々な 編集 機能をサポートしています.
ノート
GRASSレイヤを編集する手順は異なります- 詳細は GRASSベクタレイヤのデジタイジングと編集 のセクションを参照ください。
ちなみに
同時編集
QGIS のこのバージョンは誰があなたと一緒に地物の同時編集を行なっているかは追跡しません。最後に保存した人が編集権限を持ちます。
スナップ許容量と検索半径の設定¶
ベクタレイヤのジオメトリを最適に編集できるようにするため、頂点を編集する前に、スナップ許容値と検索半径を設定する必要があります。
スナッピング許容値¶
スナッピングの許容値とは接続や新規頂点入力や既存頂点移動を行いたいときに QGIS が最も近い頂点やセグメントを 検索 する場合の許容距離です. もしあなたの入力場所のスナッピング許容値内に頂点やセグメントが無い場合, QGIS は既存の頂点やセグメントにスナップさせる代わりにマウスボタンを離した場所に頂点を作成します. スナッピング許容値の設定はすべての許容値を利用するツールに影響をあたえます.
- A general, project wide snapping tolerance can be defined choosing
Settings ‣
 Options.
On Mac: go to QIS ‣
Options.
On Mac: go to QIS ‣  Preferences..., on Linux: Edit ‣
Preferences..., on Linux: Edit ‣
 Options. In the Digitizing
tab you can select between to vertex, to segment or to vertex and segment
as default snap mode. You can also define a default snapping tolerance and
a search radius for vertex edits. The tolerance can be set either in map
units or in pixels. The advantage of choosing pixels, is that the snapping
tolerance doesn’t have to be changed after zoom operations. In our small
digitizing project (working with the Alaska dataset), we define the
snapping units in feet. Your results may vary, but something on the order
of 300ft should be fine at a scale of 1:10 000 should be a reasonable
setting.
Options. In the Digitizing
tab you can select between to vertex, to segment or to vertex and segment
as default snap mode. You can also define a default snapping tolerance and
a search radius for vertex edits. The tolerance can be set either in map
units or in pixels. The advantage of choosing pixels, is that the snapping
tolerance doesn’t have to be changed after zoom operations. In our small
digitizing project (working with the Alaska dataset), we define the
snapping units in feet. Your results may vary, but something on the order
of 300ft should be fine at a scale of 1:10 000 should be a reasonable
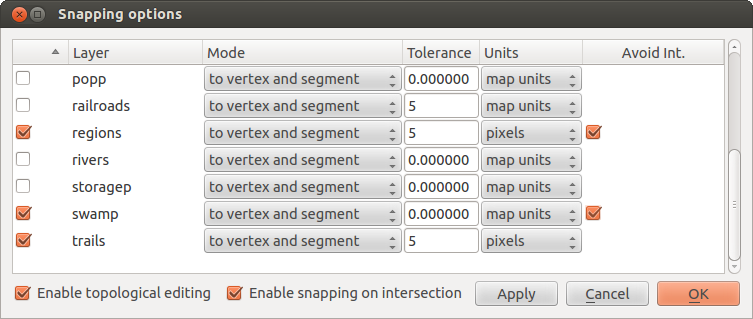
setting. レイヤ別スナッピング許容値はメニュー Settings ‣ (または File ‣) Snapping options... で指定できます.ここでレイヤ単位でスナッピングモードを有効にして許容値を調整できます (figure_edit_1 参照).
注 このレイヤ別スナッピング定義はデジタイジングタブで設定できるグローバルスナッピングオプションを上書きします.ですからあなたがあるレイヤを編集する時に他のレイヤの頂点にスナップしたい場合レイヤに対する スナップする を有効にしてグローバルスナップ許容値をそれより小さい値にする必要があります.さらにグローバルスナッピング許容値に関係なくスナッピングオプションダイアログでチェックしていないレイヤに対してはスナップできません.ですからスナップしたいレイヤについてはチェックボックスのマークに注意して下さい.
Figure Edit 1:
検索半径¶
検索半径とはあなたが地図をクリックした時に QGIS が最も近い頂点を 検索 するために使う距離です. 検索半径内に無い場合, QGIS は編集用頂点を見つけられず編集用頂点を選択できず警告がポップアップされます. スナップ許容値と検索半径は地図上の単位かピクセルで設定できます.そこで必要に応じて正しい値を設定することができます. もし大きな値を許容値に設定すると, QGIS は誤った頂点にスナップするでしょう, とりわけ多くの頂点を使うとそうなるでしょう. 検索半径を小さい値にすると何も見つからないはずでしょう.
レイヤにおける頂点編集のための検索半径の単位は Settings ‣  Options にある Digitizing タブで定義できます.同じ場所でプロジェクト全体のスナッピング許容値を定義することもできます.
Options にある Digitizing タブで定義できます.同じ場所でプロジェクト全体のスナッピング許容値を定義することもできます.
ズームとパンニング¶
レイヤを編集する前に、対象のエリアにズームすべきです。これは、すべての頂点のマーカーが全体のレイヤに描画されている間待機するのを回避します。
ツールバーにある  pan や
pan や  zoom-in /
zoom-in /  zoom-out アイコンをマウスで利用するのとは別にマウスホィールやスペースバーと矢印キーでナビゲートができますi.
zoom-out アイコンをマウスで利用するのとは別にマウスホィールやスペースバーと矢印キーでナビゲートができますi.
マウスホイールを使ったズームとパンニング¶
デジタイズを行っている間メインウィンドウでマウスホィールを使ってパンを行うことができます,そしてマウスホィールを転がすことで地図の拡大,縮小を行うことができます. 拡大を行う場合マウスカーソルを地図エリアで向こう側に(あなたと逆方向に)動かしてください,マウスカーソルを手前に(あなたのほうに)動かすと縮小します. マウスカーソルの位置はズームしたい位置の中心にあります. マウスホィールのズームの動作は  Options メニューの Settings ‣ にある Map tools タブでカスタマイズできます.
Options メニューの Settings ‣ にある Map tools タブでカスタマイズできます.
矢印キーを使ったパン¶
デジタイズ作業時に矢印キーを使ってパンを行うことができます. マウスカーソルを地図エリアにおきクリックした後右矢印キーを押すと東にパンします,左矢印キーを押すと西にパンします,上矢印キーを押すと北にパンします.下矢印キーを押すと南にパンします.
スペースバーを地図のパン作業の中断に利用できます.キーボードの PgUp と PgDown キーを使うとデジタイジング作業を中断することなく地図の拡大、縮小を行うことができます.
トポロジ編集¶
レイヤベースのスナッピングオプション定義のそばでメニュー 設定 (または ファイル) の スナップオプション... ダイアログでいくつかのトポロジカル機能の指定ができます. ここではHere you can define  トポロジ編集を有効にする の指定ができ,またポリゴンレイヤに対して
トポロジ編集を有効にする の指定ができ,またポリゴンレイヤに対して  交差禁止. の指定をすると新しいポリゴンの重なり部分が除去されます.
交差禁止. の指定をすると新しいポリゴンの重なり部分が除去されます.
トポロジ編集を有効にする¶
The option  Enable topological editing is for editing
and maintaining common boundaries in polygon mosaics. QGIS ‘detects’ a
shared boundary in a polygon mosaic and you only have to move the vertex
once and QGIS will take care about updating the other boundary.
Enable topological editing is for editing
and maintaining common boundaries in polygon mosaics. QGIS ‘detects’ a
shared boundary in a polygon mosaic and you only have to move the vertex
once and QGIS will take care about updating the other boundary.
新規ポリゴンの重なりの禁止¶
2つ目のカラムにあるトポロジカルオプションは  交差禁止. で, called 新規ポリゴンの重なり禁止 と呼ばれポリゴンモザイクでの重なりを禁止するものです. これにより隣接ポリゴンの迅速なデジタイズができます. もしあるポリゴンが存在しているところでこのオプションを使って隣接ポリゴンを重なる形でデジタイズすると QGIS は2つめのポリゴンを共通境界線で自動的にカットします.これによってユーザが共通境界線の頂点をデジタイズしなくていい利点ができます.
交差禁止. で, called 新規ポリゴンの重なり禁止 と呼ばれポリゴンモザイクでの重なりを禁止するものです. これにより隣接ポリゴンの迅速なデジタイズができます. もしあるポリゴンが存在しているところでこのオプションを使って隣接ポリゴンを重なる形でデジタイズすると QGIS は2つめのポリゴンを共通境界線で自動的にカットします.これによってユーザが共通境界線の頂点をデジタイズしなくていい利点ができます.
交差に対するスナッピングを有効にする¶
Another option is to use  Enable snapping on intersection.
It allows to snap on an intersection of background layers, even if there’s no vertex on
the intersection.
Enable snapping on intersection.
It allows to snap on an intersection of background layers, even if there’s no vertex on
the intersection.
既存レイヤのデジタイズ¶
By default, QGIS loads layers read-only: This is a safeguard to avoid accidentally editing a layer if there is a slip of the mouse. However, you can choose to edit any layer as long as the data provider supports it, and the underlying data source is writable (i.e. its files are not read-only).
一般にベクタレイヤの編集機能はデジタイジングとセクション 高度なデジタイジング で解説されている高度なデジタイジングツールバーに分けられています. 両方について 設定 ‣ ツールバー ‣ で選択、非選択を行えます. 基本的なデジタイジングツールでは以下の機能が使えます:
アイコン |
目的 |
アイコン |
目的 |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
現在の編集 |
 |
編集切り替え |
 |
地物追加 点入力 |
 |
地物追加 線入力 |
 |
地物追加 ポリゴン入力 |
 |
フィーチャの移動 |
 |
ノードツール |
 |
選択したものの削除 |
 |
フィーチャの切り取り |
 |
フィーチャのコピー |
 |
フィーチャの貼り付け |
 |
レイヤ編集の保存 |
テーブル編集 ベクタレイヤ基本編集ツールバー
すべての編集セッションは  編集モード切替 オプションを選択することで開始できます. これはそのレイヤの凡例エントリでマウス右ボタンで表示されるコンテキストメニューにあります.
編集モード切替 オプションを選択することで開始できます. これはそのレイヤの凡例エントリでマウス右ボタンで表示されるコンテキストメニューにあります.
編集モードを開始,終了する別の方法としてデジタイジングツールバーの Toggle Editing  Toggle editing ボタンを使うことができます. レイヤが編集モードになると頂点にマーカーが表示され,編集ツールバーのツールボタンが有効になります.
Toggle editing ボタンを使うことができます. レイヤが編集モードになると頂点にマーカーが表示され,編集ツールバーのツールボタンが有効になります.
ちなみに
定期的に保存する
Remember to  Save Layer Edits regularly. This will also
check that your data source can accept all the changes.
Save Layer Edits regularly. This will also
check that your data source can accept all the changes.
フィーチャの追加¶
You can use the  Add Feature,
Add Feature,
 Add Feature or
Add Feature or  Add Feature icons on the toolbar to put the QGIS cursor into
digitizing mode.
Add Feature icons on the toolbar to put the QGIS cursor into
digitizing mode.
それぞれの地物に対し、まずジオメトリをデジタイズし、属性を入力します。ジオメトリをデジタイズするには、マップエリアで左クリックし新しい地物の最初の頂点を作成します。
ラインとポリゴンで点を追加する場合は入力したい位置にマウス左ボタンでクリックを続けてください.点の追加を終了したい場合は地図上のどこかをマウス右ボタンでクリックして地物のジオメトリ入力終了を確認して下さい.
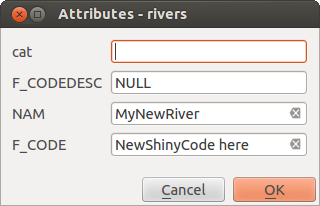
The attribute window will appear, allowing you to enter the information for
the new feature. Figure_edit_2 shows setting attributes for a fictitious new
river in Alaska. In the Digitizing menu under the
Settings ‣ Options menu, you can also activate  Suppress attributes pop-up windows after each created feature
Suppress attributes pop-up windows after each created feature
 Reuse last entered attribute values.
Reuse last entered attribute values.
Figure Edit 2:
With the  Move Feature(s) icon on the toolbar you can
move existing features.
Move Feature(s) icon on the toolbar you can
move existing features.
ちなみに
属性値タイプ
For editing the attribute types are validated during the entry. Because of this, it is not possible to enter a number into the text-column in the dialog Enter Attribute Values or vice versa. If you need to do so, you should edit the attributes in a second step within the Attribute table dialog.
現在の編集¶
This new feature allows the digitization of multiple layers. Choose
 Save for Selected Layers to save all changes you
made in multiple layers. You also have the opportunity to
Save for Selected Layers to save all changes you
made in multiple layers. You also have the opportunity to
 Rollback for Selected Layers so that the
digitization is then withdrawn for all selected layers.
If you want to stop editing the selected layers the
Rollback for Selected Layers so that the
digitization is then withdrawn for all selected layers.
If you want to stop editing the selected layers the  Cancel for Selected Layer(s)
is an easy way.
Cancel for Selected Layer(s)
is an easy way.
The same functions for editing all layers of the project are available.
ノードツール¶
For shapefile-based layers as well as SpatialLite,PostgreSQL/PostGIS, MSSQL Spatial and Oracle Spatial tables the
 Node Tool provides manipulation capabilites of
feature vertices similar to CAD programs. It is possible to simply select
multiple vertices at once and to move, add or delete them alltogether.
The node tool also works with ‘on the fly’ projection turned on and supports
the topological editing feature. This tool is, unlike other tools in
QGIS, persistent, so when some operation is done, selection stays
active for this feature and tool. If the node tool couldn’t find any
features, a warning will be displayed.
Node Tool provides manipulation capabilites of
feature vertices similar to CAD programs. It is possible to simply select
multiple vertices at once and to move, add or delete them alltogether.
The node tool also works with ‘on the fly’ projection turned on and supports
the topological editing feature. This tool is, unlike other tools in
QGIS, persistent, so when some operation is done, selection stays
active for this feature and tool. If the node tool couldn’t find any
features, a warning will be displayed.
Important is to set the property Settings ‣  Options ‣ Digitizing ‣ Search Radius:
Options ‣ Digitizing ‣ Search Radius:
 to a number greater than zero (i.e. 10). Otherwise QGIS will
not be able to tell which vertex is being edited.
to a number greater than zero (i.e. 10). Otherwise QGIS will
not be able to tell which vertex is being edited.
基本操作¶
Start by activating the  Node Tool and selecting a
feature by clicking on it. Red boxes will appear at each vertex of this feature.
Node Tool and selecting a
feature by clicking on it. Red boxes will appear at each vertex of this feature.
- Selecting vertices: You can select vertices by clicking on them one
at a time, by clicking on an edge to select the vertices at both ends, or
by clicking and dragging a rectangle around some vertices. When a vertex
is selected its color changes to blue. To add more vertices to the current
selection, hold down the
Ctrlkey while clicking. Hold downCtrlorShiftwhen clicking to toggle the selection state of vertices (vertices that are currently unselected will be selected as usual, but also vertices that are already selected will become unselected). - Adding vertices: To add a vertex simply double click near an edge and a new vertex will appear on the edge near to the cursor. Note that the vertex will appear on the edge, not at the cursor position, therefore it has to be moved if necessary.
- Deleting vertices: After selecting vertices for deletion, click the
Deletekey. Note that you cannot use the Node Tool to delete a complete feature; QGIS will ensure it retains
the minimum number of vertices for the feature type you are working on.
To delete a complete feature use the
Node Tool to delete a complete feature; QGIS will ensure it retains
the minimum number of vertices for the feature type you are working on.
To delete a complete feature use the  Delete Selected tool.
Delete Selected tool. - Moving vertices: Select all the vertices you want to move. Click on a selected vertex or edge and drag in the direction you wish to move. All the selected vertices will move together. If snapping is enabled, the whole selection can jump to the nearest vertex or line.
Each change made with the node tool is stored as a separate entry in the undo dialog. Remember that all operations support topological editing when this is turned on. On the fly projection is also supported, and the node tool provides tooltips to identify a vertex by hovering the pointer over it.
地物の切り取り、コピーと貼り付け¶
Selected features can be cut, copied and pasted between layers in the same
QGIS project, as long as destination layers are set to  Toggle editing beforehand.
Toggle editing beforehand.
Features can also be pasted to external applications as text: That is, the features are represented in CSV format with the geometry data appearing in the OGC Well-Known Text (WKT) format.
However in this version of QGIS, text features from outside QGIS cannot be
pasted to a layer within QGIS. When would the copy and paste function come
in handy? Well, it turns out that you can edit more than one layer at a time
and copy/paste features between layers. Why would we want to do this? Say
we need to do some work on a new layer but only need one or two lakes, not
the 5,000 on our big_lakes layer. We can create a new layer and use
copy/paste to plop the needed lakes into it.
例として新しいレイヤに同じ湖沼をコピーしています。
コピーしたいレイヤをロードします (ソースレイヤ)
コピー先にしたいレイヤをロードまたは作成します(ターゲットレイヤ)
ターゲットレイヤの編集を開始します
凡例をクリックしてソースレイヤをアクティブにします
- Use the
 Select Single Feature tool to select the
feature(s) on the source layer
Select Single Feature tool to select the
feature(s) on the source layer - Click on the
 Copy Features tool
Copy Features tool 判例をクリックしてコピー先レイヤをアクティブにして下さい
- Click on the
 Paste Features tool
Paste Features tool 編集モードを終了して変更内容を保存して下さい
ソースとターゲットレイヤのスキーマ(フィールド名と型が異なる場合)が異なる場合どうなるでしょうか? QGIS はマッチできる項目以外を無視します.もしあなたがターゲットレイヤにコピーする属性の内容にこだわらない場合はフィールドとデータタイプの設計は重要ではありません.すべてを - 地物とその属性 - 正しくコピーしたい場合はスキーマを一致させなければなりません.
ちなみに
貼り付け地物の一致
If your source and destination layers use the same projection, then the pasted features will have geometry identical to the source layer. However if the destination layer is a different projection then QGIS cannot guarantee the geometry is identical. This is simply because there are small rounding-off errors involved when converting between projections.
選択地物の削除¶
If we want to delete an entire polygon, we can do that by first selecting the
polygon using the regular  Select Single Feature tool. You
can select multiple features for deletion. Once you have the selection set,
use the
Select Single Feature tool. You
can select multiple features for deletion. Once you have the selection set,
use the  Delete Selected tool to delete the
features.
Delete Selected tool to delete the
features.
The  Cut Features tool on the digitizing toolbar can
also be used to delete features. This effectively deletes the feature but
also places it on a “spatial clipboard”. So we cut the feature to delete.
We could then use the
Cut Features tool on the digitizing toolbar can
also be used to delete features. This effectively deletes the feature but
also places it on a “spatial clipboard”. So we cut the feature to delete.
We could then use the  Paste Features tool to put it back,
giving us a one-level undo capability. Cut, copy, and paste work on the
currently selected features, meaning we can operate on more than one at a time.
Paste Features tool to put it back,
giving us a one-level undo capability. Cut, copy, and paste work on the
currently selected features, meaning we can operate on more than one at a time.
編集レイヤの保存¶
When a layer is in editing mode, any changes remain in the memory of QGIS.
Therefore they are not committed/saved immediately to the data source or disk.
If you want to save edits to the current layer but want to continue editing
without leaving the editing mode, you can click the  Save Layer Edits button. When you turn editing mode off with the
Save Layer Edits button. When you turn editing mode off with the
 Toggle editing (or quit QGIS for that matter),
you are also asked if you want to save your changes or discard them.
Toggle editing (or quit QGIS for that matter),
you are also asked if you want to save your changes or discard them.
If the changes cannot be saved (e.g. disk full, or the attributes have values that are out of range), the QGIS in-memory state is preserved. This allows you to adjust your edits and try again.
ちなみに
データの整合性
It is always a good idea to back up your data source before you start editing. While the authors of QGIS have made every effort to preserve the integrity of your data, we offer no warranty in this regard.
高度なデジタイジング¶
アイコン |
目的 |
アイコン |
目的 |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
アンドゥ |
 |
リドゥ |
 |
フィーチャ(群)の回転 |
 |
地物の簡素化 |
 |
リングの追加 |
 |
パートの追加 |
 |
リングの削除 |
 |
パートの削除 |
 |
地物の変形 |
 |
オフセットカーブ |
 |
地物の分割 |
 |
選択地物の結合 |
 |
ポイントシンボルの回転 |
 |
選択地物の属性の結合 |
高度なテーブル編集: ベクタレイヤの高度な編集ツールバー
アンドゥとリドゥ¶
 取り消し と
取り消し と  再実行 ツールを使うとベクタ編集操作の取り消しや再実行を行うことができます.取り消し/再実行操作の全履歴を表示できる結合表示可能なウィジェットもあります ( Figure_edit_3 参照). このウィジェットはデフォルトでは表示されていません; このウィジェットはツールバー上でマウス右ボタンをクリックして取り消し/再実行チェックボックスをアクティブにすることで表示できます. ウィジェットが表示されていなくても取り消し/再実行機能は有効です.
再実行 ツールを使うとベクタ編集操作の取り消しや再実行を行うことができます.取り消し/再実行操作の全履歴を表示できる結合表示可能なウィジェットもあります ( Figure_edit_3 参照). このウィジェットはデフォルトでは表示されていません; このウィジェットはツールバー上でマウス右ボタンをクリックして取り消し/再実行チェックボックスをアクティブにすることで表示できます. ウィジェットが表示されていなくても取り消し/再実行機能は有効です.
Figure Edit 3:
When Undo is hit, the state of all features and attributes are reverted to the state before the reverted operation happened. Changes other than normal vector editing operations (for example changes done by a plugin), may or may not be reverted, depending on how the changes were performed.
To use the undo/redo history widget simply click to select an operation in the history list; all features will be reverted to the state they were in after the selected operation.
フィーチャ(群)の回転¶
Use the  Rotate Feature(s) to rotate one or multiple
selected features in the map canvas. You first need to select the features
and then press the
Rotate Feature(s) to rotate one or multiple
selected features in the map canvas. You first need to select the features
and then press the  Rotate Feature(s) Icon. Then the
centroid of the feature appears and will be the rotation anchor point. If you selected
multiple features the rotation anchor point will be the common center of the features.
Press and drag the left mouse button in the desired direction to rotate the
selected features.
Rotate Feature(s) Icon. Then the
centroid of the feature appears and will be the rotation anchor point. If you selected
multiple features the rotation anchor point will be the common center of the features.
Press and drag the left mouse button in the desired direction to rotate the
selected features.
It’s also possible to create a user-defined rotation anchor point by which the selected feature will rotate.
Select the features to rotate and activate the  Rotate Feature(s) Tool.
Press and hold the
Rotate Feature(s) Tool.
Press and hold the Ctrl button and move the mouse pointer (without pressing the mouse button)
to the place where you want the rotation anchor to be moved. Release the Ctrl button
when the desired rotation anchor point is reached. Now press and drag the left mouse button
in the desired direction to rotate the selected feature(s).
地物の簡素化¶
The  Simplify Feature tool allows to reduce the
number of vertices of a feature, as long as the geometry doesn’t change.
You need to select a feature, it will be highlighted by a red rubber band
and a slider appears. Moving the slider, the red rubber band is changing
its shape to show how the feature is being simplified. Clicking [OK]
the new, simplified geometry will be stored. If a feature cannot be simplified
(e.g. MultiPolygons), a message shows up.
Simplify Feature tool allows to reduce the
number of vertices of a feature, as long as the geometry doesn’t change.
You need to select a feature, it will be highlighted by a red rubber band
and a slider appears. Moving the slider, the red rubber band is changing
its shape to show how the feature is being simplified. Clicking [OK]
the new, simplified geometry will be stored. If a feature cannot be simplified
(e.g. MultiPolygons), a message shows up.
リングの追加¶
You can create ring polygons using the  Add Ring icon in the toolbar. This means inside an existing area it
is possible to digitize further polygons, that will occur as a ‘hole’, so
only the area in between the boundaries of the outer and inner polygons remain
as a ring polygon.
Add Ring icon in the toolbar. This means inside an existing area it
is possible to digitize further polygons, that will occur as a ‘hole’, so
only the area in between the boundaries of the outer and inner polygons remain
as a ring polygon.
パートの追加¶
You can  add part polygons to a selected
multipolygon. The new part polygon has to be digitized outside
the selected multipolygon.
add part polygons to a selected
multipolygon. The new part polygon has to be digitized outside
the selected multipolygon.
リングの削除¶
The  Delete Ring tool allows to delete ring polygons
inside an existing area. This tool only works with polygon layers. It doesn’t
change anything when it is used on the outer ring of the polygon. This tool
can be used on polygon and multi-polygon features. Before you select the
vertices of a ring, adjust the vertex edit tolerance.
Delete Ring tool allows to delete ring polygons
inside an existing area. This tool only works with polygon layers. It doesn’t
change anything when it is used on the outer ring of the polygon. This tool
can be used on polygon and multi-polygon features. Before you select the
vertices of a ring, adjust the vertex edit tolerance.
パートの削除¶
The  Delete Part tool allows to delete parts from
multifeatures (e.g. to delete polygons from a multipolygon feature). It won’t
delete the last part of the feature, this last part will stay untouched. This
tool works with all multi-part geometries point, line and polygon. Before you
select the vertices of a part, adjust the vertex edit tolerance.
Delete Part tool allows to delete parts from
multifeatures (e.g. to delete polygons from a multipolygon feature). It won’t
delete the last part of the feature, this last part will stay untouched. This
tool works with all multi-part geometries point, line and polygon. Before you
select the vertices of a part, adjust the vertex edit tolerance.
地物の変形¶
You can reshape line and polygon features using the  Reshape Features icon on the toolbar. It replaces the line or polygon
part from the first to the last intersection with the original line. With
polygons this can sometimes lead to unintended results. It is mainly useful
to replace smaller parts of a polygon, not major overhauls and the reshape
line is not allowed to cross several polygon rings as this would generate an
invalid polygon.
Reshape Features icon on the toolbar. It replaces the line or polygon
part from the first to the last intersection with the original line. With
polygons this can sometimes lead to unintended results. It is mainly useful
to replace smaller parts of a polygon, not major overhauls and the reshape
line is not allowed to cross several polygon rings as this would generate an
invalid polygon.
For example, you can edit the boundary of a polygon with this tool. First, click in the inner area of the polygon next to the point where you want to add a new vertex. Then, cross the boundary and add the vertices outside the polygon. To finish, right-click in the inner area of the polygon. The tool will automatically add a node where the new line crosses the border. It is also possible to remove part of the area from the polygon, starting the new line outside the polygon, adding vertices inside, and ending the line outside the polygon with a right click.
ノート
The reshape tool may alter the starting position of a polygon ring or a closed line. So the point that is represented ‘twice’ will not be the same any more. This may not be a problem for most applications, but it is something to consider.
オフセットカーブ¶
The  Offset Curve tool creates parallel shifts of line layers.
The tool can be applied to the edited layer (the geometries are modified)
or also to background layers (creates copies of the lines / rings and adds it to the the edited layer).
It is thus ideally suited for the creation of distance line layers. The displacement is
shown at the bottom left of the taskbar.
To create a shift of a line layer you have to go into editing mode and then
select the feature. You can make the
Offset Curve tool creates parallel shifts of line layers.
The tool can be applied to the edited layer (the geometries are modified)
or also to background layers (creates copies of the lines / rings and adds it to the the edited layer).
It is thus ideally suited for the creation of distance line layers. The displacement is
shown at the bottom left of the taskbar.
To create a shift of a line layer you have to go into editing mode and then
select the feature. You can make the  Offset Curve tool active and drag
the cross to the desired distance. Your changes then can be saved with the
Offset Curve tool active and drag
the cross to the desired distance. Your changes then can be saved with the
 Save Layer Edits tool.
Save Layer Edits tool.
地物の分割¶
ツールバー上の  Split Features アイコンを使って地物を分割できます. 分割したい地物を交差する線を描画すれば分割できます.
Split Features アイコンを使って地物を分割できます. 分割したい地物を交差する線を描画すれば分割できます.
選択フィーチャのマージ¶
The  Merge Selected Features tool allows to merge
features that have common boundaries and the same attributes.
Merge Selected Features tool allows to merge
features that have common boundaries and the same attributes.
選択地物の属性マージ¶
The  Merge Attributes of Selected Features tool
allows to merge attributes of features with common boundaries and
attributes without merging their boundaries.
You can merge the attributes when selecting several features at once. Then
press the
Merge Attributes of Selected Features tool
allows to merge attributes of features with common boundaries and
attributes without merging their boundaries.
You can merge the attributes when selecting several features at once. Then
press the  Merge Attributes of Selected Features button.
Now QGIS offers you which attributes are to be applied to all selected objects.
As a result, all objects have the same attribute entries.
Merge Attributes of Selected Features button.
Now QGIS offers you which attributes are to be applied to all selected objects.
As a result, all objects have the same attribute entries.
ポイントシンボルの回転¶
The  Rotate Point Symbols allows to change the rotation
of point symbols in the map canvas. You have to define a rotation column
from the attribute table of the point layer in the Advanced menu of the
Style menu of the Layer Properties. Also you have to
go into the ‘SVG marker’ and choose Data defined properties ....
Activate
Rotate Point Symbols allows to change the rotation
of point symbols in the map canvas. You have to define a rotation column
from the attribute table of the point layer in the Advanced menu of the
Style menu of the Layer Properties. Also you have to
go into the ‘SVG marker’ and choose Data defined properties ....
Activate  Angle and choose ‘rotation’ as field.
Without these settings the tool is inactive.
Angle and choose ‘rotation’ as field.
Without these settings the tool is inactive.
Figure Edit 4:
To change the rotation, select a point feature in the map canvas and rotate it holding the left mouse button pressed. A red arrow with the rotation value will be visualized (see Figure_edit_4). When you release the left mouse button again, the value will be updated in the attribute table.
ノート
If you hold the Ctrl key pressed, the rotation will be done in 15
degree steps.
新しいベクタレイヤの作成¶
QGIS では新規の Shapefile レイヤを作ることができます, 新規 SpatiaLite レイヤと新規GPX レイヤを作ることができます. 新規 GRASSレイヤの作成はGRASS-pluginででサポートされています. GRASS ベクタレイヤ作成の詳しい情報はセクション 新しいGRASSベクターレイヤーの作成 を参照して下さい.
新規Shapefileレイヤの作成¶
To create a new Shape layer for editing, choose New ‣
 New Shapefile Layer... from the
Layer menu. The New Vector Layer dialog will be
displayed as shown in Figure_edit_5. Choose the type of layer (point, line or
polygon) and the CRS (Coordinate Reference System).
New Shapefile Layer... from the
Layer menu. The New Vector Layer dialog will be
displayed as shown in Figure_edit_5. Choose the type of layer (point, line or
polygon) and the CRS (Coordinate Reference System).
注 QGIS はまだ 2.5D 地物の作成をサポートしていません (例. X,Y,Z座標を持つ地物).
Figure Edit 5:
To complete the creation of the new Shapefile layer, add the desired attributes
by clicking on the [Add to attributes list] button and specifying a name and type for the
attribute. A first ‘id’ column is added as default but can be removed, if not
wanted. Only Type: real  , Type: integer
, Type: integer
 , Type: string
, Type: string  and Type:date
and Type:date  attributes are supported. Additionally and according to the attribute type you can also define
the width and precision of the new attribute column. Once you are happy with
the attributes, click [OK] and provide a name for the shapefile. QGIS will
automatically add a
attributes are supported. Additionally and according to the attribute type you can also define
the width and precision of the new attribute column. Once you are happy with
the attributes, click [OK] and provide a name for the shapefile. QGIS will
automatically add a .shp extension to the name you specify. Once the
layer has been created, it will be added to the map and you can edit it in the
same way as described in Section 既存レイヤのデジタイズ above.
新規Spatialiteレイヤの作成¶
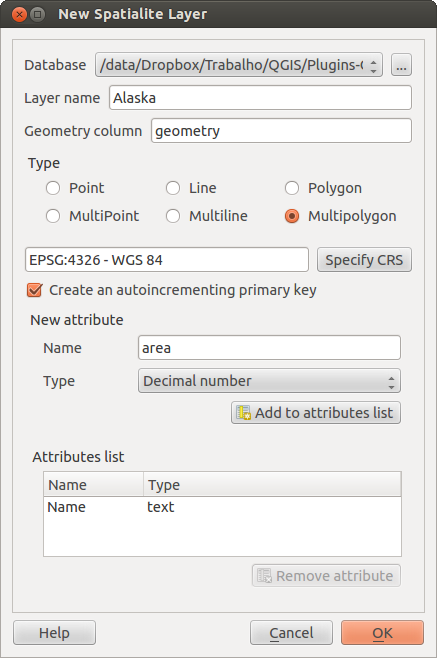
To create a new SpatiaLite layer for editing, choose New ‣
 New SpatiaLite Layer... from the
Layer menu. The New SpatiaLite Layer dialog will
be displayed as shown in Figure_edit_6.
New SpatiaLite Layer... from the
Layer menu. The New SpatiaLite Layer dialog will
be displayed as shown in Figure_edit_6.
Figure Edit 6:
First step is to select an existing SpatiaLite database or to create a new
SpatiaLite database. This can be done with the browse button  to
the right of the database field. Then add a name for the new layer and define
the layer type and specify the Coordinate Reference System with [Specify CRS].
If desired you can select to
to
the right of the database field. Then add a name for the new layer and define
the layer type and specify the Coordinate Reference System with [Specify CRS].
If desired you can select to  Create an autoincrementing primary key.
Create an autoincrementing primary key.
To define an attribute table for the new SpatiaLite layer, add the names of the attribute columns you want to create with the according column type and click on the [Add to attribute list] button. Once you are happy with the attributes, click [OK]. QGIS will automatically add the new layer to the legend and you can edit it in the same way as described in Section 既存レイヤのデジタイズ above.
SpatiaLite-Layers の高度な管理はDB マネージャを使うと実行できます DB マネージャプラグイン 参照.
新しいGPXレイヤの作成¶
新しい GPXファイルを作成するためには GPS プラグインを最初にロードする必要があります. Plugins ‣  Plugin Manager... で Plugin Manager ダイアログを開いてください.
Plugin Manager... で Plugin Manager ダイアログを開いてください.  GPS Tools チェックボックスをアクティブにして下さい.
GPS Tools チェックボックスをアクティブにして下さい.
このプラグインがロードされると:menuselection:Layer`メニューで :menuselection:`New –>  Create new GPX Layer... を選択できます. Save new GPX file as ダイアログで新しい GPX レイヤを保存する場所を選べます.
Create new GPX Layer... を選択できます. Save new GPX file as ダイアログで新しい GPX レイヤを保存する場所を選べます.
属性テーブルの作業¶
The attribute table displays features of a selected layer. Each row in the table represents one map feature and each column contains a particular piece of information about the feature. Features in the table can be searched, selected, moved or even edited.
To open the attribute table for a vector layer, make the layer active by
clicking on it in the map legend area. Then from the main menu
Layer choose  Open Attribute
Table. It is also possible to rightclick on the layer and choose
Open Attribute
Table. It is also possible to rightclick on the layer and choose
 Open Attribute Table from the dropdown menu
and to click on the
Open Attribute Table from the dropdown menu
and to click on the  Open Attribute Table button
in the Attributes toolbar.
Open Attribute Table button
in the Attributes toolbar.
This will open a new window which displays the feature attributes in the layer (figure_attributes_1). The number of features and the number of selected features are shown in the attribute table title.
Figure Attributes 1:
属性テーブルにおける地物の選択¶
Each selected row in the attribute table displays the attributes of a selected feature in the layer. If the set of features selected in the main window is changed, the selection is also updated in the attribute table. Likewise, if the set of rows selected in the attribute table is changed, the set of features selected in the main window will be updated.
Rows can be selected by clicking on the row number on the left side of the
row. Multiple rows can be marked by holding the Ctrl key.
A continuous selection can be made by holding the Shift key and
clicking on several row headers on the left side of the rows. All rows
between the current cursor position and the clicked row are selected.
Moving the cursor position in the attribute table, by clicking a cell in the
table, does not change the row selection. Changing the selection in the main
canvas does not move the cursor position in the attribute table.
The table can be sorted by any column, by clicking on the column header. A small arrow indicates the sort order (downward pointing means descending values from the top row down, upward pointing means ascending values from the top row down).
For a simple search by attributes on only one column choose the Column filter ‣ from the menu in the bottom left corner. Select the field (column) from which the search should be performed from the dropdown menu and hit the [Apply] button. Then only the matching features are shown in the Attribute table.
To make a selection you have to use the ![]() Select features using an Expression
icon on top of the Attribute table.
The
Select features using an Expression
icon on top of the Attribute table.
The ![]() Select features using an Expression allows you
to define a subset of a table using a Function List like in the
Select features using an Expression allows you
to define a subset of a table using a Function List like in the
 Field Calculator (see フィールド計算機).
The query result then can be saved as a new vector layer.
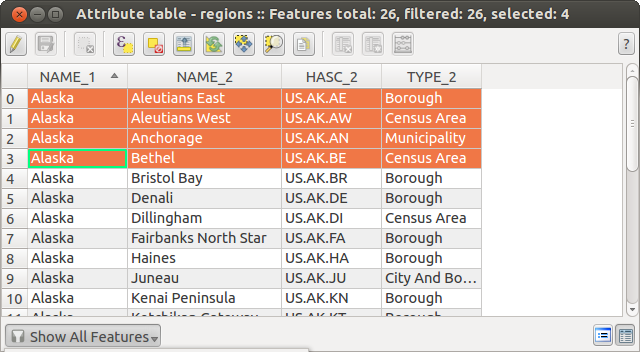
For example if you want to find regions that are boroughs from the regions.shp
of the QGIS sample data you have to open the >Fields and Values menu
and choose the field that you want to query. Double-klick the field ‘TYPE_2’ and also
[Load all unique values] . From list choose and double-klick ‘Borough’.
In the Expression field the following query appears:
Field Calculator (see フィールド計算機).
The query result then can be saved as a new vector layer.
For example if you want to find regions that are boroughs from the regions.shp
of the QGIS sample data you have to open the >Fields and Values menu
and choose the field that you want to query. Double-klick the field ‘TYPE_2’ and also
[Load all unique values] . From list choose and double-klick ‘Borough’.
In the Expression field the following query appears:
"TYPE_2" = 'Borough'
The matching rows will be selected and the total number of matching rows will appear in the title bar of the attribute table, and in the status bar of the main window. For searches that display only selected features on the map use the Query Builder described in Section クエリビルダー.
選択されたレコードのみを表示したい場合右下のメニューの Show Selected Features を利用して下さい.
属性テーブルの上部にあるその他のボタンは以下のような機能を提供しています:
選択地物を新規レイヤに保存する¶
選択した地物は任意のOGRがサポートしたベクタフォーマットとして保存され、別の座標参照系(CRS)に変換することができます。レイヤのコンテキストメニューを開き 選択を名前をつけて保存 ‣ をクリック後、出力ファイルの名称、フォーマット、CRSを定義します。( :ref:`label_legend`のセクションを参照)。ダイアログ内でOGR作成オプションを指定することも可能です。
空間的でない属性テーブルの作業¶
QGIS では空間情報が無いテーブルをロードすることができます. この機能は OGRでサポートされているテーブルや, デリミテッドテキストと同じように PostgreSQL, MSSQL とOracle プロバイダで利用できます. テーブルに対してフィールドのルックアップや一般的な閲覧,編集をテーブルビューで行うことができます. テーブルをロードすると凡例フィールドに表示されます. これはたとえば  Open Attribute Table ツールで開くことができ他の属性テーブルと同じように編集できます.
Open Attribute Table ツールで開くことができ他の属性テーブルと同じように編集できます.
As an example you can use columns of the non spatial table to define attribute values or a range of values that are allowed to be added to a specific vector layer during digitizing. Have a closer look at the edit widget in section フィールドメニュー to find out more.